HLD002 - Combined Network Model
Introduction
Purpose
The purpose of this document is to outline the high-level design architecture for AWS Network with centralized Inspection VPC, distributed inbound and concept of shared VPCs. This model, called Combined Network provides a secure and isolated environment for conducting network inspections and assessments, with increased throughput and flexibility.
Changelog
Revision | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 01.07.2024 | Initial document |
Related documents
Background
Combined model for AWS Network refers to a network architecture where a central VPC is used to conduct network inspections, while other AWS resources, such as EC2 instances, databases, and storage systems, are located in separate VPCs. The inspection VPC acts as a centralized hub for conducting network assessments and inspections, while the other resources are isolated and protected from potential security threats. Distributed ingress deployment avoids bottlenecks and increases high-availability, as systems doesn't rely on single Internet Gateway.
Centralized AWS Network model includes:
Inspection VPC: Used for centralized management of network security, routing and access control, as well as for resource isolation and cost optimization. Inspection VPC acts as edge connection to the Internet or on-premise network, Firewall and IDS/IPS data source.
Public VPC: Isolated virtual network where resources are accessible from the Internet. In a public VPC, subnets have direct access to the Internet through an Internet Gateway (IGW), allowing resources within these subnets to communicate with external networks. Public IP addresses are associated with resources in public subnets, enabling inbound Internet traffic.
Private VPC: Isolated virtual network designed to host resources without direct access to the Internet. In a private VPC, subnets are connected to a Transit Gateway (TGW), ensuring secure communication with on-premises networks or other VPCs. Private VPCs are ideal for sensitive workloads, internal applications, and secure data storage, providing a controlled and secure network environment within the AWS ecosystem.
Isolated VPC: Virtual network architecture designed to provide an additional layer of security by segregating resources and traffic within a strictly controlled environment. Isolated VPCs are not connected to the Internet or other VPCs, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive data and applications. By leveraging Network ACLs, Security Groups, and VPC endpoints, Isolated VPCs enable secure access to specific AWS services while maintaining a high level of isolation, making them suitable for compliance-sensitive workloads and stringent security requirements.
Sandbox VPC: Isolated virtual network dedicated to experimentation, development, and testing of applications and infrastructure. Sandbox VPCs provide a safe environment, separate from production workloads, where developers can deploy resources, explore new technologies, and validate configurations without impacting critical systems.
Transit Gateway (TGW): Acts as a central point of connectivity, allowing customers to manage traffic between VPCs and data centers using a single connection. The Transit Gateway provides a scalable and highly available solution for managing network traffic and allows customers to simplify their network architecture, reduce complexity, and improve security.
Direct Connect (DX): Dedicated network service that establishes a private, low-latency connection between your on-premises data center and AWS. Bypassing the public Internet, DX offers consistent network performance, increased data transfer speeds, end enhanced security, making it an ideal solution for hybrid cloud architectures and critical workloads.
Internet Gateway (IGW): Allows communication between our AWS environment and the Internet. It acts as a bridge between the VPC and the Internet, allowing resources to securely receive inbound traffic from the Internet and route outbound to the Internet.
NAT Gateway (NGW): Allows instance in a private subnet to access the Internet, while preventing the Internet from initialing a connection with those instances. This helps increase the security of the network and ensure that only authorized traffic is allowed in and out of the instances.
Gateway LoadBalancer (GWLB): Offers transparent load balancing and centralized deployment of security and network appliances, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and deep packet inspection systems. GWLB simplifies the management of traffic flows and ensures optimal performance, reliability, and security for applications.
Gateway LoadBalancer Endpoint (GWLB Endpoint): Enables seamless traffic distribution from VPCs to the Gateway LoadBalancer. It functions as a network target within a VPC, allowing clients to sent traffic without traversing the Internet or AWS backbone.
Firewall instance: Virtual security appliance deployed on an EC2 instance. It filters and manages network traffic based on predefined rules, integrates with services like GWLB and VPC Ingress Routing, and provides scalable, centralized protection.
Web Application Firewall (WAF): Protects web applications and APIs from threats like SQL Injection, XSS, and DDoS attacks. With customizable security rules, AWS WAF filters and controls traffic based on conditions such as IP addresses and HTTP headers. It integrates with AWS services like API Gateway, Application LoadBalancer, and CloudFront for improved security and performance.
Implementation Details
Architecture diagram
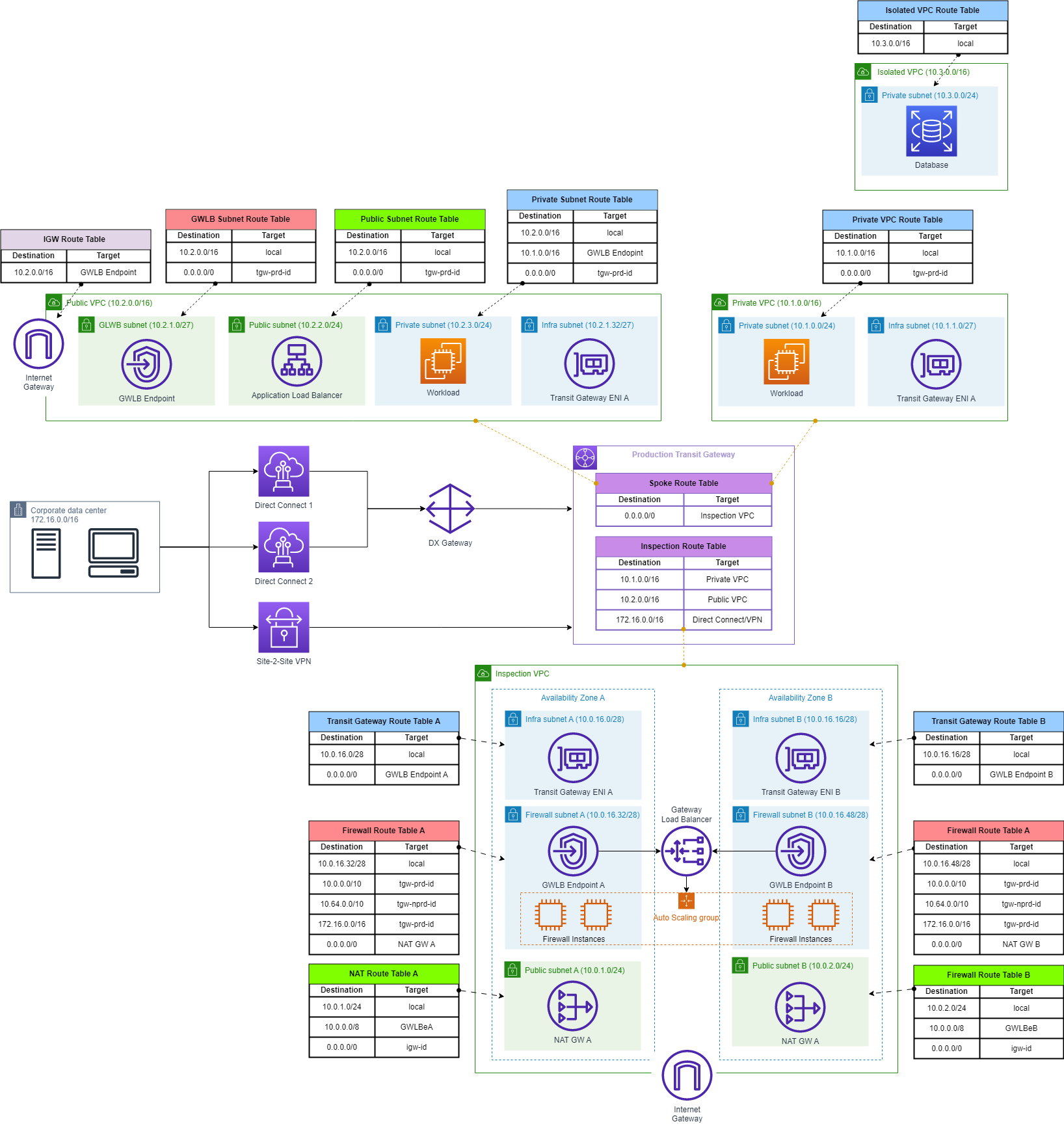
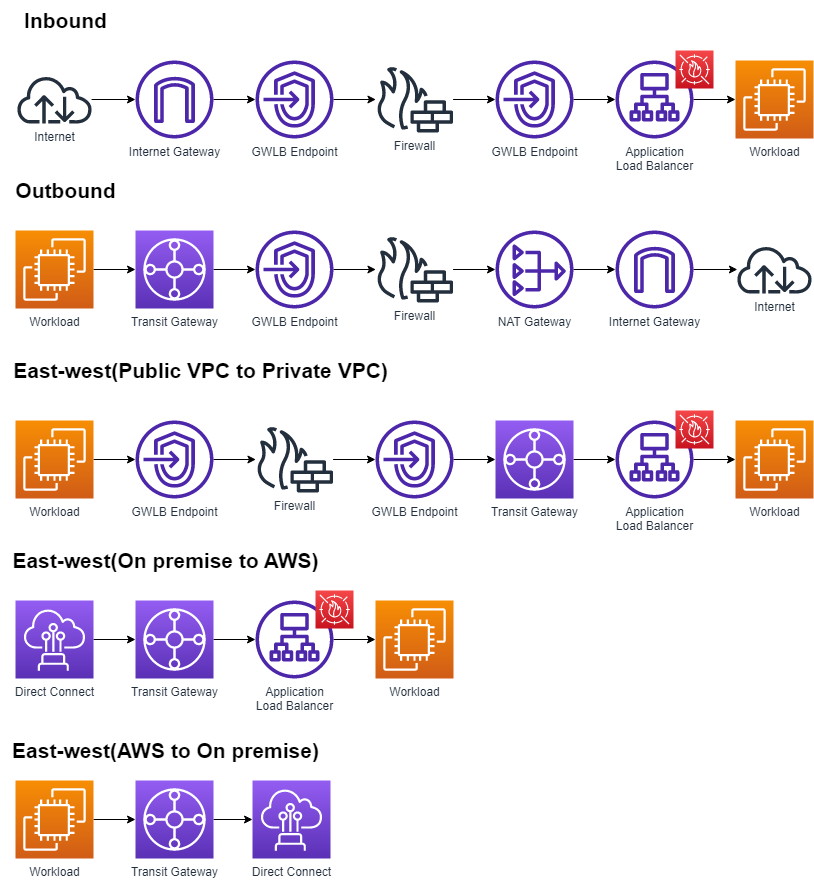
This diagram represents the architecture of the Combined AWS Network implementation. It shows basic schema of components correlations, connections and route tables.
Inspection VPC
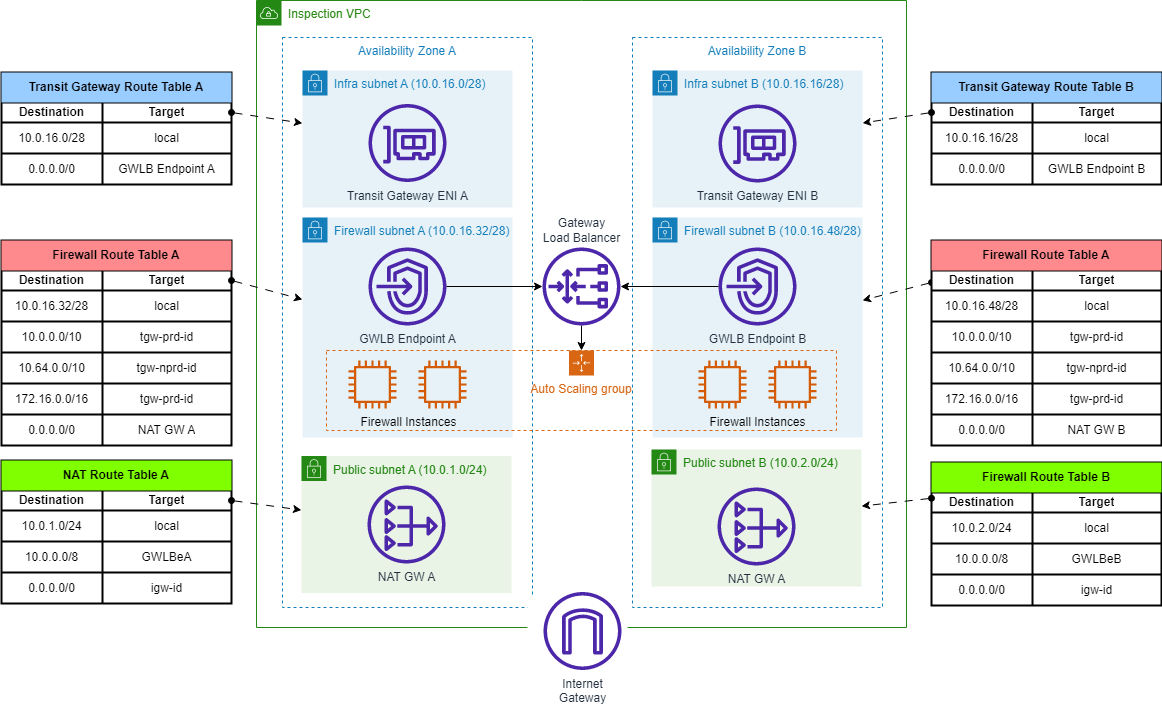
The Inspection VPC consists of three subnets in each AZs:
Infra Subnet
Firewall Subnet.
Public Subnet.
To achieve fault-tolerant implementation, it's recommended to use at least two Availability Zones As NAT Gateway, Firewall instances and TGW attachments does not across multiple AZs, it's needed to create separated copies in each AZ.
Each TGW subnet requires a dedicated VPC route table to ensure the traffic is forwarded to the GWLB endpoint within the same AZ. These route tables have a default route (0.0.0.0/0) pointing towards the GWLB endpoints in the same AZ.
Workloads VPCs
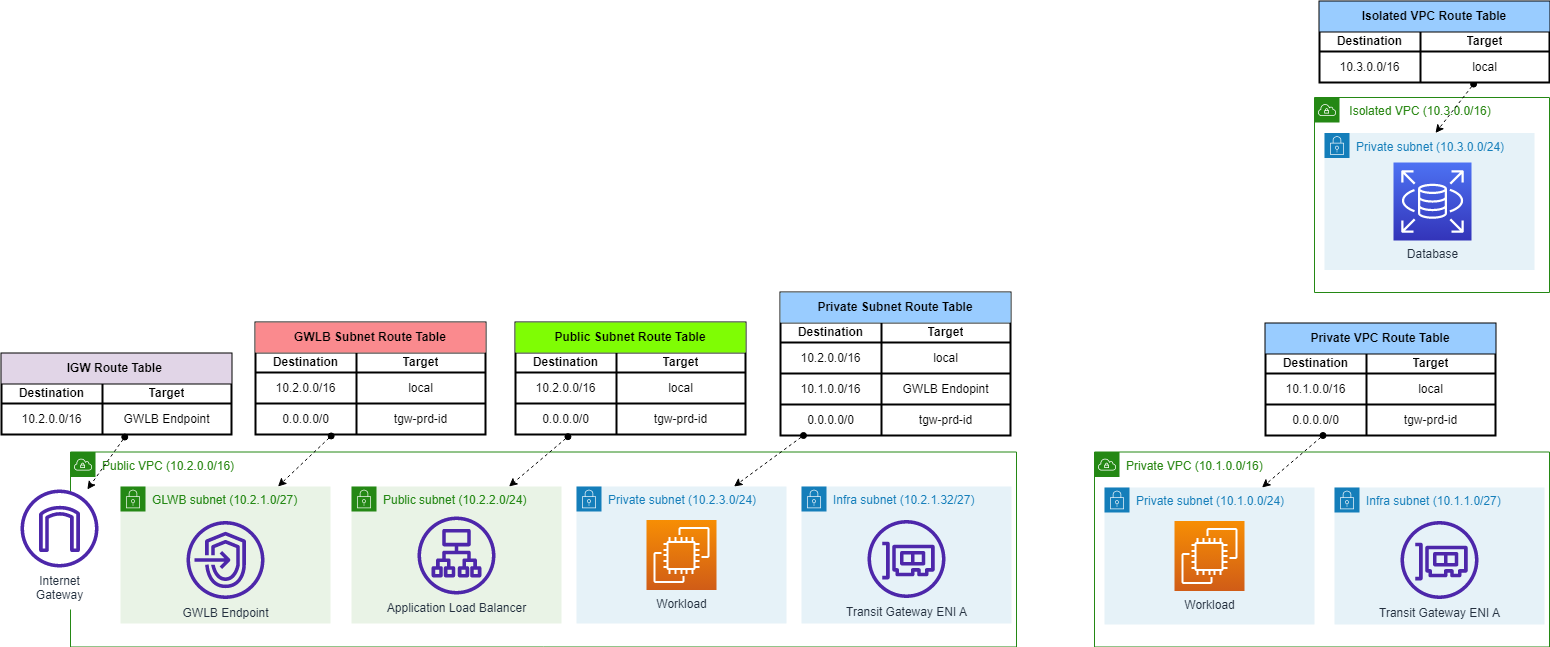
Workloads VPCs are dedicated for infrastructure systems and application workloads. It contains dedicated VPCs in configurations:
Public VPC
Private VPC
Isolated VPC
Public and Private VPCs are used to host workloads and shared-services software. Each VPC is attached with AWS Transit Gateway for hub-and-spoke configuration. The default route 0.0.0.0/0 in the VPC route tables towards Transit Gateway ensures any egress traffic will travel through the Inspection VPC.
In addition, Public VPC has its own Internet Gateway for ingress traffic incoming from Internet. Packets from IGW are redirected to Firewall solution via GWLB Endpoint for inspection, then send back to workloads infrastructure.
Traffic from the frontend to the backend undergoes inspection through a firewall via the GWLB endpoint. This ensures stringent security measures, faciliating close monitoring and control over the data transmitted between the frontend and backend systems.
Isolated VPC is detached from any source of connection.
Transit Gateway and Direct Connect
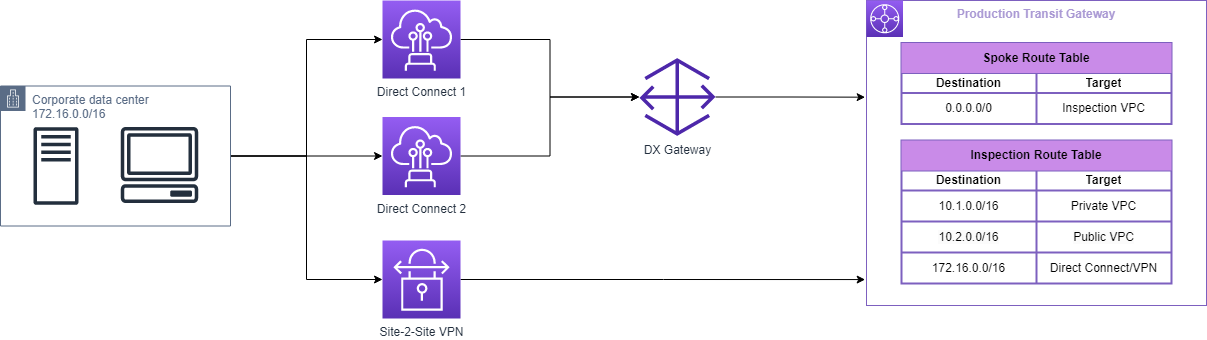
AWS Transit Gateway acts as a network hub and simplifies the connectivity between VPCs as well as on-premises networks. AWS Transit Gateway also provides inter-region peering capabilities to other TGW to establish a global network.
Redundant AWS Direct Connect connections are utilized to provide a consistent and reliable network experience, while Site-to-Site VPN serves as backup, ensuring connectivity in case of DX outages. This configuration not only increases network resilience byt also provides an encrypted connection for data transmission, enhancing overall security.
Integrating a DX gateway with a TGW offers advantages for enterprise networking, including improved performance, simplified management, enhanced security, and grater scalability. This approach provides dedicated connectivity between on-premises data centers and cloud resources, encrypts traffic, and allows for easy network scaling without reconfiguring topology.
TGW route tables are used to route traffic between TGW attachments deployed in VPC. For better view, it's recommended to use multiple separated route tables per environment layer.
For this simple scenario we use:
Spoke Route Table. Spoke VPCs are associated with this route table.
Route external Spoke VPC traffic to Inspection VPC.
Inspection Route Table. Inspection VPC is associated with this route table.
Private VPC CIDR route with Private VPC attachments as the target.
Public VPC CIDR route with Public VPC attachment as the target.
On-premise CIDR route with DX as the target.
Connection flow
Secure Content Delivery and Dynamic Workloads
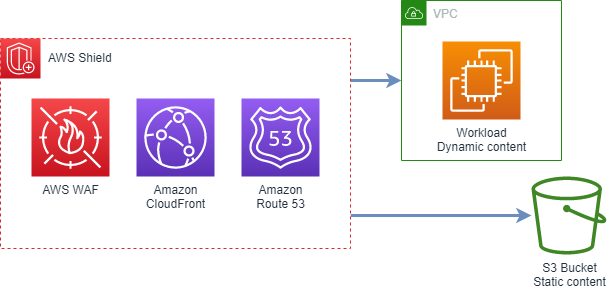
AWS Shield Advanced
AWS Shield Advanced is employed for comprehensive protection against larger and more sophisticated attacks. As a managed Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) protection service, AWS Shield Advanced provides always-on detection and automatic in-line mitigations to minimize application downtime and latency. This premium service also offers cost protection and 24/7 DDoS response team (DRT) access during an event, along with advanced threat intelligence for heightened security.
AWS Web Application Firewall
Serving as a protective layer, AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF) safeguards the application from common web exploits. By controlling access to the content, AWS WAF prevents malicious attempts to compromise the security of applications or data, or to consume resources excessively, thereby mitigating potential cost increases.
Amazon CloudFront
AWS content delivery network (CDN) service speeds up the distribution of web content to end-users. It achieves this by caching static content at edge locations worldwide, reducing latency and increasing loading speeds. Furthermore, CloudFront is designed to work seamlessly with dynamic, interactive content and serverless computing services, ensuring a responsive user experience.
Layers od security and management tools
AWS Firewall Manager
AWS Firewall Manager is a centralized security management service that simplifies the administration of security rules and policies across multiple accounts and resources within AWS organization. By integrating with AWS WAF, AWS Shield Advanced, and Amazon VPC security groups, Firewall Manager enables consistent enforcement of security policies, ensuring protection against common threats like DDoS attacks, malicious web traffic and unauthorized access. It offers streamlined configuration, automated auditing, and real-time monitoring, providing a unified solution for maintaining security posture across entire AWS infrastructure.
Tuffin
Tuffin's orchestration suite is leveraged to manage and automate Network Access Control Lists (NACLs) and other security configurations across the network infrastructure. It is an alternative to AWS Firewall Manager, but it can also work in parallel. Tuffin's software enables visualization of the network topology, control of access permissions, and streamlined compliance with security policies. By centralizing management and providing automation capabilities, Tuffin significantly simplifies the task of maintaining network security and compliance in complex, heterogeneous environments.
NACL
NACL is a security layer that acts as a firewall to allow or deny traffic based on rules that you define. NACLs are used to add a layer od security to your VPC by filtering inbound and outbound traffic based on IP addresses, ports, and protocols.
Depending on account distribution, dedicated NACLs will be created, for example:
NACL for private account, allowing access only from a public account CIDRs.
NACL for database subnet, allowing access only from private subnet CIDRs.
NACL for private subnet, allowing access only from database and public subnet CIDRs.
NACL for public subnet, denying access from database subnet CIDRs, allowing access from the Internet.
In addition, NACL can block traffic between individual accounts that should not send traffic between each other, e.g. between prod and dev accounts.
Security Groups
AWS Security Groups are virtual firewalls that control inbound and outbound traffic to resources, such as EC2 instances, within VPC. They act as a set of rules defining which traffic is allowed or denied at the instance level, based on parameters like IP addresses, ports, and protocols. Security Groups enable granular access control, ensuring that only authorized traffic can reach your resources, thereby enhancing the overall security of your AWS environment. They are stateful, meaning that anny allowed inbound traffic automatically permits corresponding outbound traffic, simplifying network management and maintaining secure communication between resources.
For very sensitive environments (confidential information, etc.) there may be a requirement for redundant mirroring of rules from other systems to SG/NACL.
Traffic monitoring
VPC Flowlogs
VPC Flowlogs is an AWS feature that captures, stores, and analyzes network traffic within a VPC. It enables granular monitoring at the VPC, subnet, or network interface level and stores data in S3 or CloudWatch Logs. This tool aids in network troubleshoot issues, optimize request routing, and enhance the security analysis, and compliance audits while offering customization and integration with other AWS services and third-party tools.
Access Logs
Access logs record detailed information about requests made to load balancer, including client IP addresses, request paths, response codes, and processing times. By analyzing access logs, administrators can troubleshoot issues, optimize request routing, and enhance the security of load balancer.
Expected Outcomes
Secure setup of AWS environment Network.
Centralized Internet connection.
Established connections between Spoke VPCs.
Implemented network firewall.