HLD003 - Continous Compliance
Introduction
This high-level design document provides an overview of the compliance strategy leveraging AWS Config, AWS Security Hub and Amazon Guard Duty. The primary goal is to ensure that the organization's infrastructure on the AWS platform is secure, compliant, and adheres to industry best practices.
AWS Config
Overview
AWS Config is a fully managed service that provides continuous monitoring and assessment of AWS resources to ensure compliance with best practices and law requirements. It tracks resource changes, evaluate configurations against defined guidelines, and maintains a detailed history of AWS resources configuration and compliance. It also gives possibility to create both manual and automated remediation for non-compliant resources.
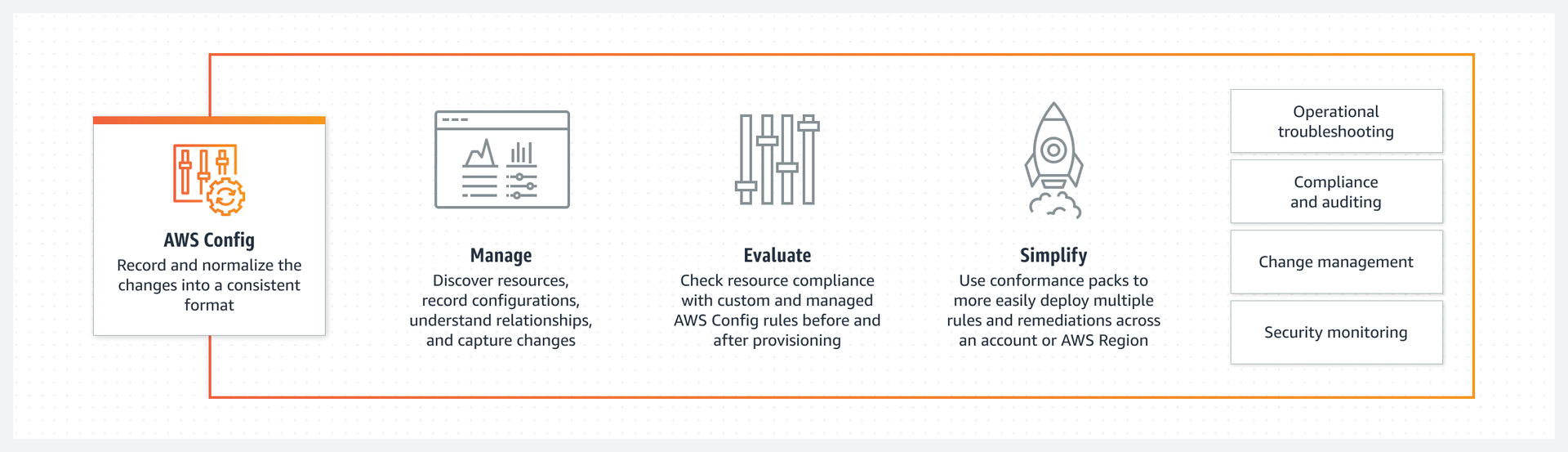
Key Components
Configuration Recorder: The Configuration Recorder collects data about AWS resources and their configurations. It stores the data as configuration items.
Rules: Rules evaluate resource configurations against desired settings, providing real-time compliance assessments. AWS Config supports both AWS managed rules and custom rules.
Conformance Packs: Conformance Packs are collections of AWS Config rules and remediation actions that help organizations achieve compliance with specific regulatory standards, industry best practices, or internal guidelines. They cen be easily deployed and managed across multiple accounts and regions.
Aggregators: Aggregators provide a unified view of resource configurations and compliance across multiple AWS accounts and regions.
Resource Inventory: The Resource Inventory allows for a comprehensive view of all AWS resources and their past and current configurations. It serves as a single source of truth for resource data.
Advanced Queries: Advanced Queries enable users to search, filter, and analyze resource configuration data using SQL-like syntax. This functionality helps with infrastructure management, const optimization, security and compliance.
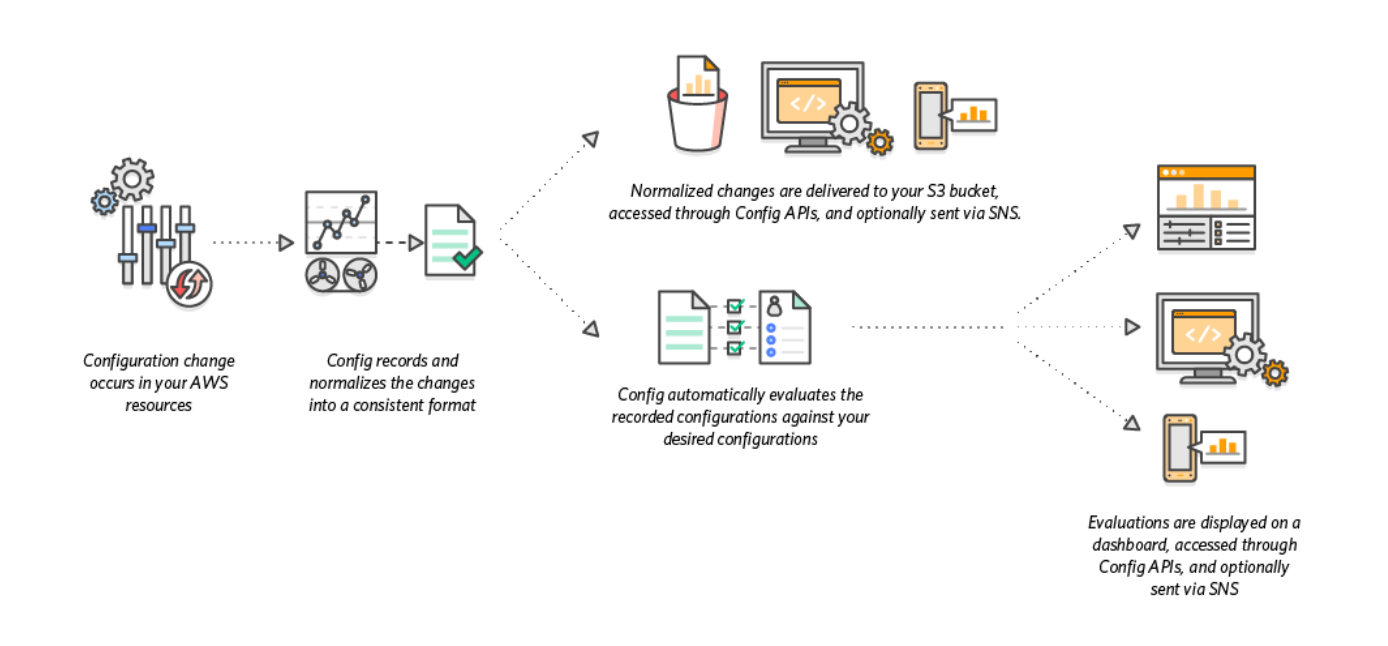
Workflow
AWS Config continuously discovers, records, and evaluates resource configurations against defined Configuration Rules. Every time here is a change in AWS resources, AWS Config records it and creates new Configuration Item with current resource configuration.
Each resource change triggers rules that evaluates current resource state. For every rule non-compliant resource can trigger a remediation that will execute a set of actions like triggering alerts, sending notifications, changing resource configurations and more.
Implementation Details
Identify and evaluate the security issue: Review available rules and conformance packs, compare them to rules deployed by Security Hub, determine which rules will by implemented.
Decide on remediation plan: each rule ca be associated with remediation plan. Remediation can be either manual or automatic. Remediation used in AWS Config are System Manager Automation Documents, which contain all logic. Remediation are optional. It might be redundant to set up remediation in both AWS Config and Security Hub.
Implement AWS Config: Enable AWS Config and deploy chosen conformance packs/rules/remediation.
Monitor and maintain: Monitor the compliance of your environment with deployed conformance packs and rules. Use AWS Config Dashboard or AWS Security Hub Findings to ensure your AWS environment remains secure and compliant.
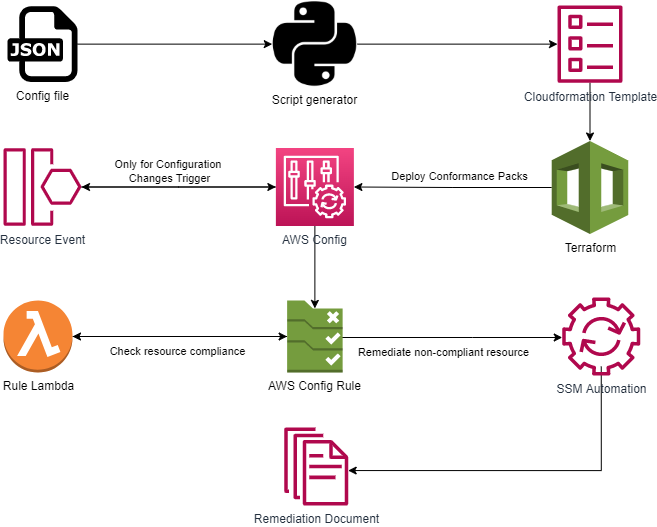
Custom Config Deployment Solution
For AWS Config implementation "Custom Config Deployment Solution" will be used.
"Custom Config Deployment Solution" was developed to make creation of Conformance Packs faster and much simpler. Solution is based on Python script that loads configuration files and generates Cloudformation Template, that is used for deployment of AWS Config conformance packs, rules and associated resources lke AWS Lambda Functions for custom rules or Systems Manager Documents for custom remediation.
Amazon Guard Duty
Overview
Amazon GuardDuty is a security monitoring service that analyses and processes data sources, such as AWS CloudTrail data events for Amazon S3 logs, CloudTrail management event logs, DNS logs, Amazon EBS volume data, Kubernetes audit logs, Amazon VPC flow logs, and RDS login activity. It uses threat intelligence fees, such as lists of malicious IP addresses and domains, and machine learning to identify unexpected, potentially unauthorized, and malicious activity within your AWS environment. This can include issues like escalation of privileges, use of exposed credentials, or communication with malicious IP addresses, domains, presence of malware on your Amazon EC2 instances and container workloads, or discovery of unusual patterns of login events on your database. For example, GuardDuty can detect compromised EC2 instances and container workloads serving malware, or mining bitcoin. It also monitors AWS account access behaviour for signs of compromise, such as unauthorized infrastructure deployments, like instances deployed in a Region that hasn't been used before, or unusual API calls like a password policy change to reduce password strength.
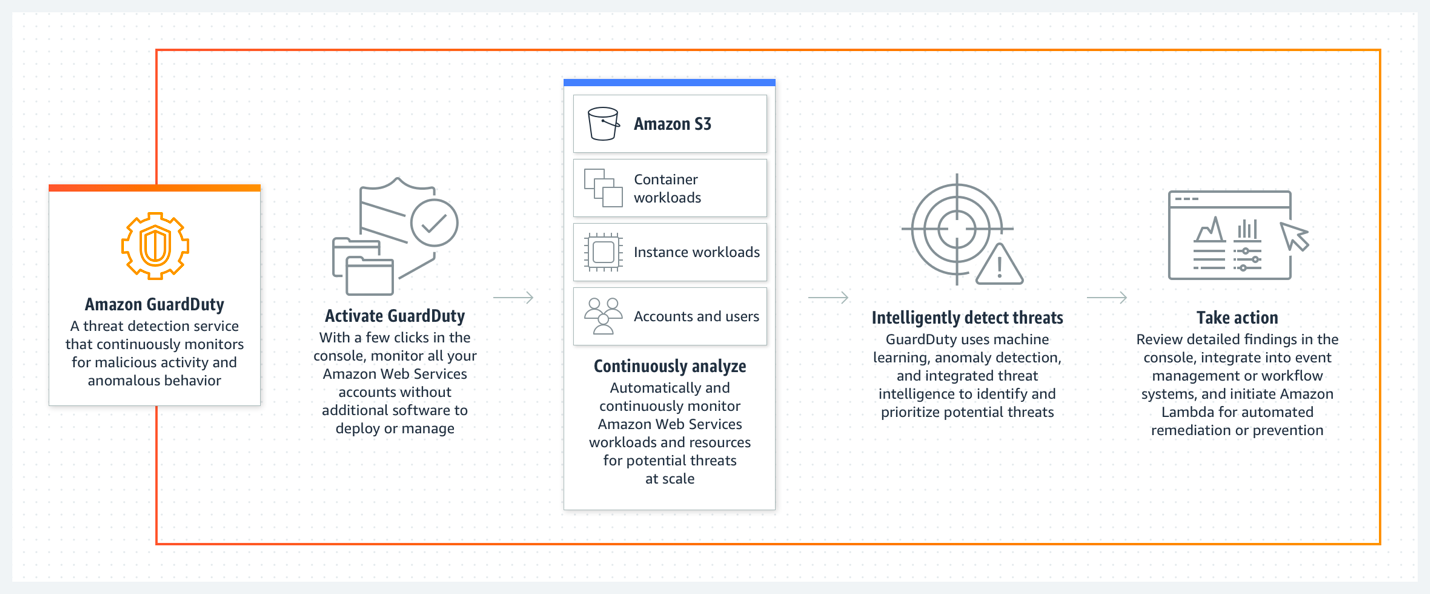
Key Components
Data Sources: GuardDuty analyzes data from various sources such as AWS CloudTrail logs, VPC Flow Logs, and DNS logs to detect potential threats.
Findings: GuardDuty generates findings based on the analysis of the collected data. Findings include details about the threat, affected resources, and recommended remediation steps.
Threat Intelligence: GuardDuty integrates with various threat intelligence feeds and continuously updates its knowledge base to identify known malicious IP addresses, domains, and other indicators of compromise.
Machine Learning: GuardDuty leverages machine learning algorithms to detect anomalies and unusual behaviour in your AWS environment, helping identify potential security issues.
Data Sources
List of data sources:
Workflow
GuardDuty automatically collects and analyzes data from enabled AWS services and data sources. Using a combination of threat intelligence and machine learning, GuardDuty identifies potential security threats. Upon detecting a threat GuardDuty generates findings with details about the threat and affected resources. Every new finding is sent to AWS Security Hub. User can check findings in GuardDuty console page or in AWS Security Hub Findings dashboard.
AWS Security Hub
Overview
AWS Security Hub is a centralised service that helps identify and prioritise security risks across an organization's AWS environment. It collects, aggregates, and analyzes security findings from various AWS services and supported third-party partner products, providing a comprehensive view of the infrastructure security state.
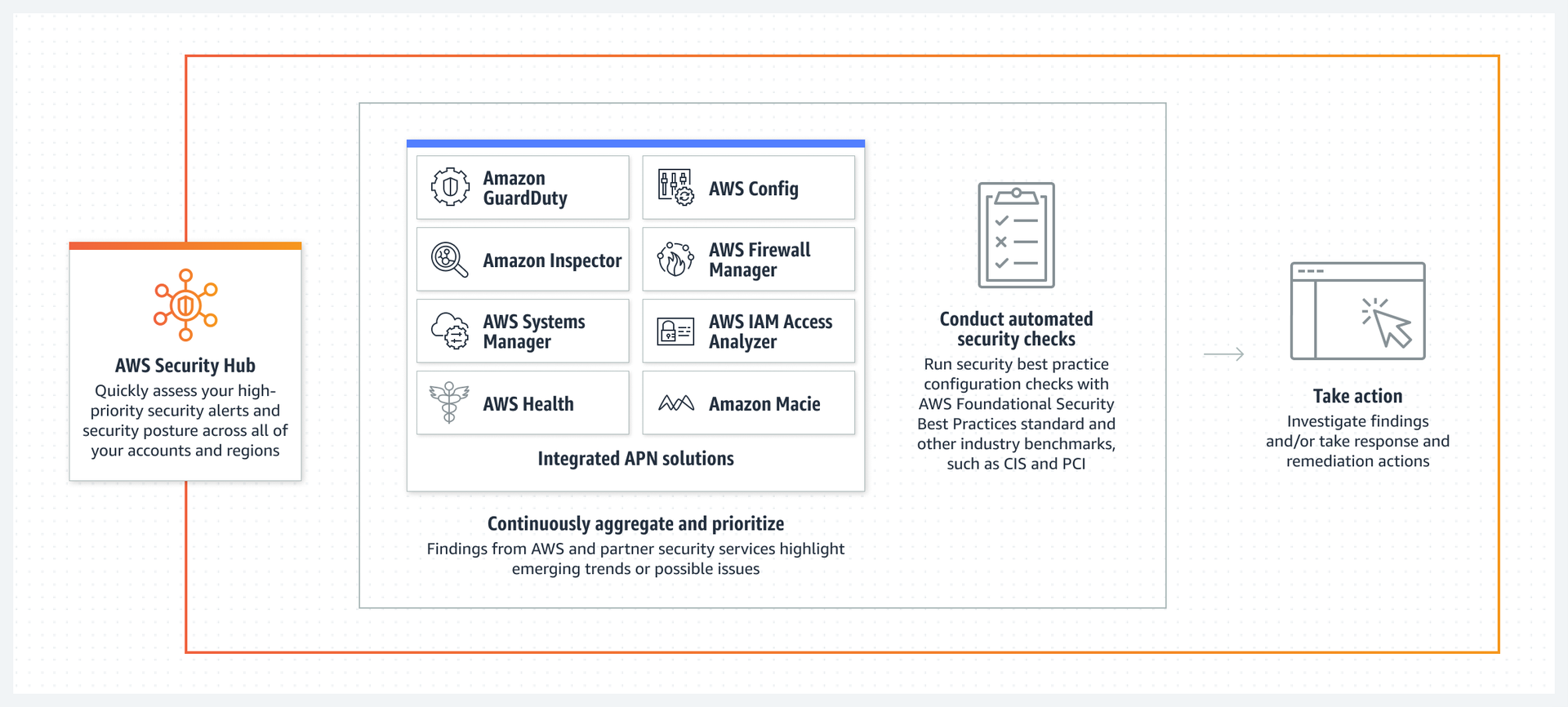
Key Components
Findings: Findings are the security issues detected by AWS Security Hub or integrated AWS services and partner products. Each finding is associated with a severity level and a set of metadata to facilitate analysis and remediation. It is a tool prepared for monitoring/security teams for simple management of infrastructure.
Insights: Insights are a collections of related findings, that help identify security trends, patterns, and potential issues in the AWS environment.
Controls: Controls are specific security requirements and recommendations within a standard. They provide a basis for evaluating the compliance of AWS resources and help organizations align their security practices with industry best practices or regulatory requirements. Most of the controls are associated with AWS Config rules that are managed by Security Hub.
Security Standards: Standards are predefined security frameworks, such as CIS AWS Foundations or PCI DSS, which are used to evaluate and measure the security posture of organization. Standards consist of set of controls.
Workflow
AWS Security Hub aggregates compliance results for many services. Every time there is an issue sent from one of these services, Security Hub creates a Finding with details about non-compliant resource. Each new findings can trigger a custom remediation, using Amazon EventBridge.
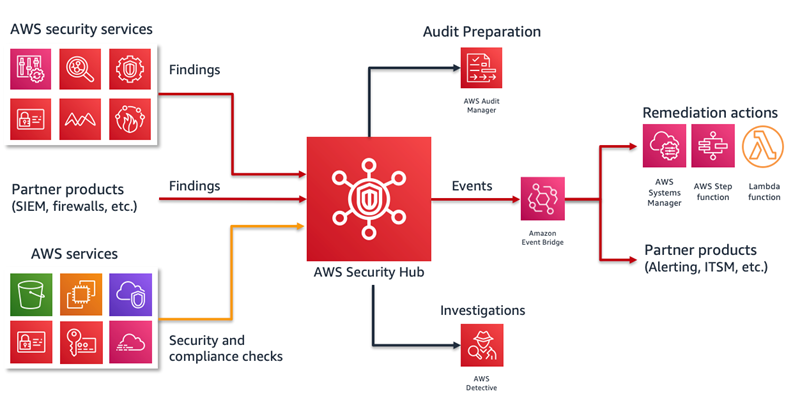
Implementation Details
Identify and evaluate the security issues: Review CIS AWS Benchmark and determine which controls are applicable to environment. It's recommended to use all the controls is CIS AWS Foundations Benchmark v1.4.0 and AWS Foundational Security Best Practices standards, with few exceptions described in official documentation.
Chose remediation plan: Each control requires remediation plan. Remediation can be either manual or automatic. Environment owner should decide what kind of action takes place to meet security requirements. AWS provides information about recommended remediation methods for most of the controls in official documentation.
Implement remediation plans: Enable Security Hub and implement the security actions as outlined in the remediation plan.
Monitor and maintain: Monitor the security controls to ensure they continue to be effective over time. Regularly review the CIS AWS Benchmark and other security standards to ensure that your AWS environment remains secure and compliant.
Custom Security Hub Deployment Solution
For AWS Security Hub implementation "Custom Security Hub Deployment Solution" will be used.
"Custom Security Hub Deployment Solution" was developed to make creation and deployment of Security Hub with remediation quick and simple. Solution is based on Python script that loads configuration files and generates terraform template, that is used for deployment EventBridge Rules, AWS Lambda Functions and associating them with defined controls and findings types.
Solution Features:
Enabling Security Hub.
Setting up cross-account aggregation.
Augmenting Security hub findings from various services with additional, service-specific information ex. copying resource tags to resource-related findings.
Setting up automating remediation:
filtering based on findings details.
email notifications.
SNS notifications.
custom Lambda remediation.
Automatically suppressing false-positives based on regex matches or exact values of:
finding details.
resource tags.
resource ARNs.
Compliance - Remediation
Although AWS Config, Amazon GuardDuty and AWS Security Hub can set up automatic remediation, it is recommended to centralise remediation by using AWS Security Hub exclusively. Security Hub remediation can address issues generated from other security services as well. Managing remediation individually for each service would be more complex and challenging to organise. For this reason, AWS Config and Amazon GuardDuty will serve as the backbone for identifying issues in AWS infrastructure, while AWS Security Hub events wil be responsible for remediating them.
Amazon prepared documentation for Amazon GuardDuty describing suggested ways od remediating found threats and issues.
Expected Outcomes
Implemented continuous compliance with AWS Config, AWS Security Hub and Amazon Guard Duty.
Automatic remediation reacting to non-compliant resources.
Compliance monitoring dashboards (in both, Config and Security Hub).