Terraform
Revision | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 24.07.2024 | Init Changelog |
Introduction

Terraform is an infrastructure as code tool that lets you build, change, and version infrastructure safely and efficiently. This includes low-level components like compute instances, storage, and networking; and high-level components like DNS entries and SaaS features.
Basic informations
Here you have some useful informations about Terraform:
How it works
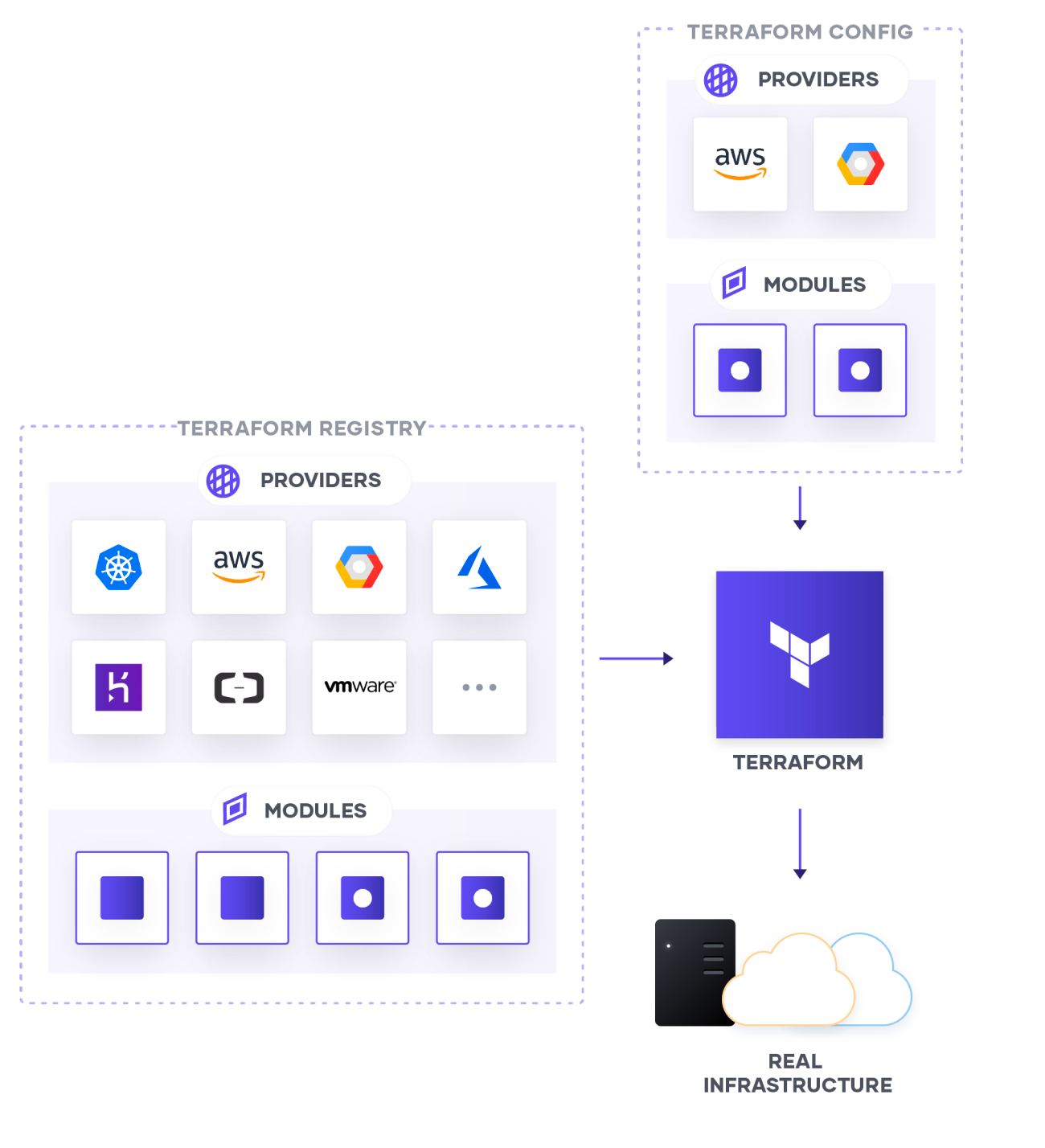
Terraform provisions, updates, and destroys infrastructure resources such as physical machines, VMs, network switches, containers, and more.
Configurations are code written for Terraform, using the human-readable HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL) to describe the desired state of infrastructure resources.
Providers are the plugins that Terraform uses to manage those resources. Every supported service or infrastructure platform has a provider that defines which resources are available and performs API calls to manage those resources.
Modules are reusable Terraform configurations that can be called and configured by other configurations. Most modules manage a few closely related resources from a single provider.
The Terraform Registry makes it easy to use any provider or module. To use a provider or module from this registry, just add it to your configuration; when you run terraform init, Terraform will automatically download everything it needs.
How to use internal modules
If you build your own Terraform Module and deploy it to internal terraform registry (on Gitlab), you need to configure your Terraform CLI on local machine to use it properly.
Create (or modify if you have one) file: ~/.terraformrc (yes, ~/ means you need to create it in your $HOME). Fill created file with content below:
If you done preparation, you can start using your module:
You can check source address of Terraform Module by going to its remote repository on Gitlab. Next go to: Operate → Terraform modules. There are provision instructions when you check package details.
Addons
With great tools, comes great community. And it creates lots of tools to make it even more useful! Below there are some of them.
tfenv
tfenv is Terraform version manager. It allows to install and switch between few Terraform versions. It is useful when you need to run old code which is not compatible with latest version.
Installation
Install via Homebrew
Usage
tfenv install [version]Installs specific Terraform version.
tfenv install tfenv install 0.7.0 tfenv install latest tfenv install latest:^0.8 tfenv install latest-allowed tfenv install min-requiredtfenv use [version]Switch to specific Terraform version.
tfenv use tfenv use min-required tfenv use 0.7.0 tfenv use latest tfenv use latest:^0.8tfenv uninstall [version]Uninstall specific Terraform version.
tfenv uninstall 0.7.0 tfenv uninstall latest tfenv uninstall latest:^0.8tfenv listList all installed Terraform versions.
tfenv list * 0.10.7 (set by /opt/tfenv/version) 0.9.0-beta2 0.8.8 0.8.4tfenv list-remoteList installable versions.
tfenv list-remote 0.9.0-beta2 0.9.0-beta1 0.8.8 0.8.7 0.8.6 0.8.5 ...
Known problems
Official Terraform binary installed as dependency with Homebrew
Some tools needs official Terraform binary installed as dependency (using Homebrew) - like Terragrunt. Having tfenv and terraform installed can cause problems during updates - Homebrew doesn’t update Terraform cause it’s path is override and it will skip other tools update.
To avoid conflict just unlink tfenv using Homebrew, do updates and link it again:
TFLint
TFLint is a pluggable Terraform Linter. TFLint has bundled Ruleset for Terraform Language.
It inspects files under the current directory and outputs report on terminal.
Installation
Install via Homebrew
Configuration
The bundled plugin enabled the “recommended” preset by default, but you can disable the plugin or use a different preset. Declare the plugin block in .tflint.hcl like this:
See the tflint-ruleset-terraform documentation for more information.
Usage
Check User Guide for more.
tfsec
tfsec is a static analysis security scanner for Terraform code.
Installation
Install via Homebrew
Usage
The easiest way to run tfsec is to run it in the directory you want to scan:
If you want to run on specific location, this can be passed as an argument:
Check --help for more.
terraform-docs
terraform-docs is a utility to generate documentation from Terraform modules in various output formats.
Installation
Install via Homebrew
Usage
Example of generating documentation for Markdown file with output on screen:
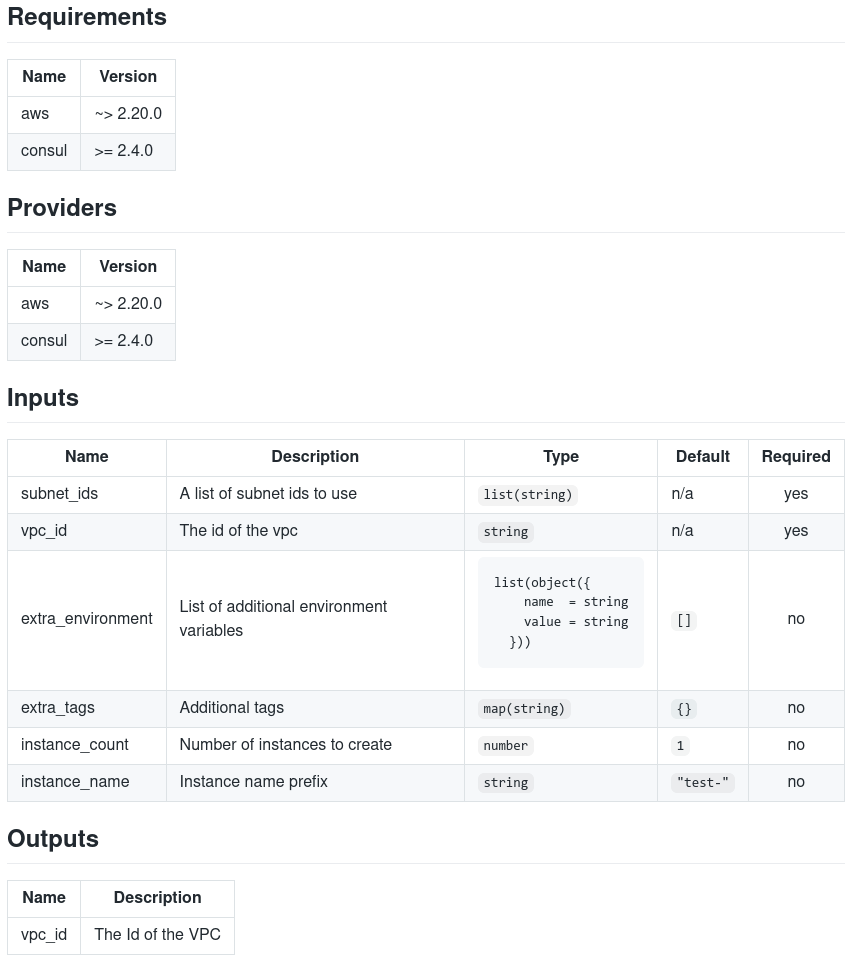
One of most popular format is markdown table, which is the best for generating README od module.
which produces:
Configuration
You can have consistent execution through a .terraform-docs.yml file.
Once you set it up and configured it, every time you or your teammates want to regenerate documentation (manually, through a pre-commit hook, or as part of a CI pipeline) all you need to do is run terraform-docs /module/path.
Read all about configuration.
Ready configs for other tools
pre-commit
Here is basic pre-commit configuration for Terraform Module repository:
.pre-commit-config.yaml
It will:
generate module documentation with
terraform-docsformat module files with
terraform fmtlint module files with
tflintvalidate module resources with
terraform validaterun security scan for module with
tfsec
terraform-docs
Here is basic terraform-docs configuration for Terraform repository:
.terraform-docs.yml
It will generate documentation and puts it in README.md.
Gitlab Pipeline (CI/CD)
Terraform Module - test, scan & deploy
Here is basic Gitlab Pipeline configuration:
.gitlab-ci.yml