LLD002-004 - Inter Region connection
Introduction
Purpose
This document presents an architecture for interconnecting cloud resources across multiple AWS regions using AWS Transit Gateway. The solution enables secure and efficient cross-region networking, enhancing data sharing and disaster recovery.
Changelog
Revision | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 10.07.2024 | Initial document |
Related documents
Background
This architecture leverages multi-region AWS deployment using Transit Gateways. Utilizing multiple regions enhances data redundancy and improves disaster recovery by allowing rapid failover. The architecture's design ensures robust performance and high availability of services, critical for business continuity.
Architecture diagram
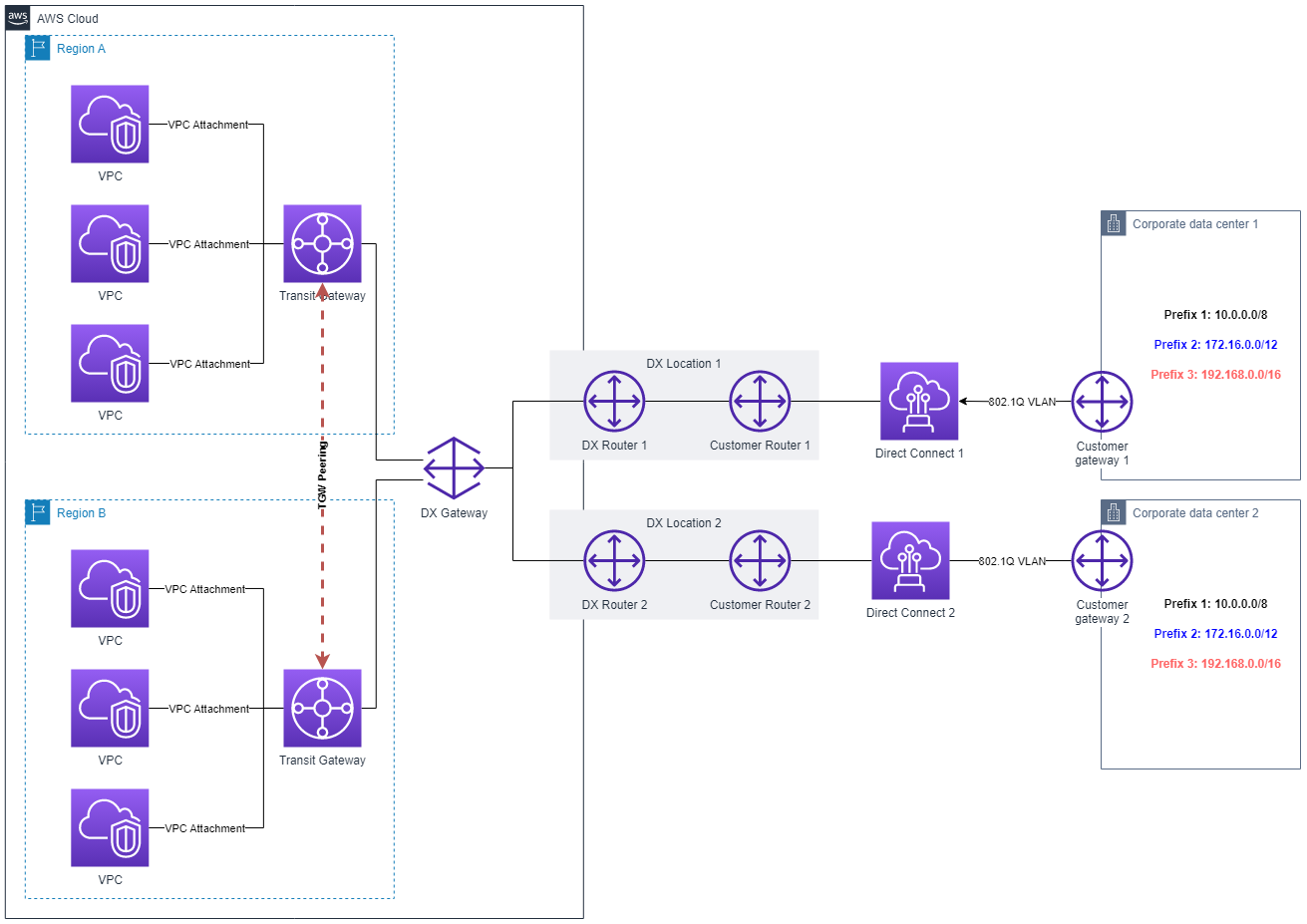
Explanation
Direct Connections: The two direct connections are high-speed data links that bypass the public internet and provide a more reliable, faster, and lower latency connection to the AWS network. The two direct connections are connected to two different data centers, providing redundancy and failover options.
DX Gateway: The Direct Connect (DX) Gateway is a hub that aggregates various virtual interfaces (VIFs) enabling connections to multiple AWS services across different regions via the Direct Connect links. This functionality simplifies bandwidth sharing across multiple AWS services and the management of these links.
Transit Gateways: Transit gateways are used to interconnect VPCs and on-premises networks. They provide a single gateway to route traffic across multiple VPCs and VPN connections. Each transit gateway is within a specific region and can connect to VPCs in the same region.
Peering Connections: Peering connections between the two transit gateways enable the routing of traffic from one transit gateway to another, effectively connecting the two different regions. These peering connections are used to share routes between the transit gateways.
Implementation Details
The critical component of this cross-region network is Transit Gateway peering. Peering involves establishing a connection between two Transit Gateways in different AWS regions, allowing them to route traffic to each other. Each peering connection is established between two Transit Gateways, and these connections can be established from any Transit Gateway to any other, enabling a fully meshed network design.
Transit Gateway peering is a secure and highly efficient mechanism to interconnect resources in different regions. It provides secure communication since traffic remains on the global AWS backbone and never traverses the public internet. Peering connections also provide high bandwidth and low-latency links between regions, which are vital for applications that require real-time or near real-time data synchronization.
Setup
Additional Transit Gateway Setup: If not already set up, establish a Transit Gateway in the secondary AWS region ( DR site) and connect it with the existing DX Gateway.
Peering Connection Setup: Create a peering connection between the Transit Gateways in the primary and secondary regions to facilitate inter-region routing of traffic in case of a disaster.
Routing Configuration: Confirm the correct routing configuration in the DX Gateway and the Transit Gateways to ensure smooth data flow.
Connectivity Flow
Data starts from on-premise network and travels through a Direct Connect (DX) link to the DX Gateway. From there, it is routed to the appropriate AWS service via the Transit Gateway in the primary region. In a standard scenario, the secondary region (DR site) stays passive. However, in a disaster situation, if the primary region fails, the system switches to the DR region. The data then travels through the peering connection to the Transit Gateway in the DR region and onto the respective VPCs. This ensures minimal downtime and data loss during a disaster.
Failover Procedure
Failure Detection: Monitoring services such as Amazon CloudWatch are employed to oversee the health of the primary region continuously. Alarms can be set to notify of any detected failures.
DR Activation: Upon detection of a failure, the disaster recovery procedure is triggered. This could involve an automated process where AWS Lambda functions are initiated by CloudWatch alarms to start the failover process.
Route Updates: To redirect incoming traffic towards the secondary region (DR site), the route tables associated with the DX Gateway need to be modified. This entails updating the route tables to direct traffic from the DX Gateway to the secondary region's Transit Gateway and the associated VPCs.
Service Verification: Post-failover, comprehensive system checks are conducted to confirm that all services are functioning correctly in the DR region. This might involve automated health checks, end-to-end testing of applications, or manual checks.
Security and Compliance
Security within this design is a paramount concern. Each VPC and Transit Gateway employs security groups and network access control lists (ACLs) to control inbound and outbound traffic. The Transit Gateways operate on the principle of the least privilege, admitting only necessary traffic. Moreover, to enhance data security, sensitive traffic may be encrypted in transit.
Scalability and Future Direction
The design lends itself to future expansion. As the system scales, additional VPCs and AWS regions can be incorporated into the existing architecture with relative ease by creating new Transit Gateways and establishing appropriate peering connections.
Expected Outcomes
Improved Disaster Recovery: The multi-region model allows for quick failover to a functioning region if one region experiences a failure, enhancing business continuity.
Enhanced Data Redundancy: Duplication of data across multiple regions can protect against data loss and ensure data availability, even if one region goes offline.
Increased Network Efficiency: The use of Transit Gateways simplifies the network structure, streamlines inter-region traffic flow, and reduces operational overhead.
Scalability: The model's design is inherently scalable, allowing additional VPCs and regions to be added as needed, in line with business growth and expansion.