HLD005 - DNS in AWS
Introduction
Purpose
This high-level design document provides a roadmap for the implementation of Route53 DNS within a Hybrid Cloud Architecture. This design ensures seamless interconnectivity between on-premises infrastructure and provides a resilient, highly available, and scalable solution that meets the organization's needs.
Changelog
Revision | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 23.07.2024 | Initial document |
Related documents
Background
Amazon Route 53 is a scalable DNS service by AWS, offering domain name registration, DNS routing, and health checking. It translates domain names into IP addresses to route end users to internet applications. Route 53 also provides DNS resolver services, enabling hybrid cloud setups by seamlessly resolving DNS queries between on-premise networks and VPCs. Additionally, it offers DNS Firewall for enhanced security.
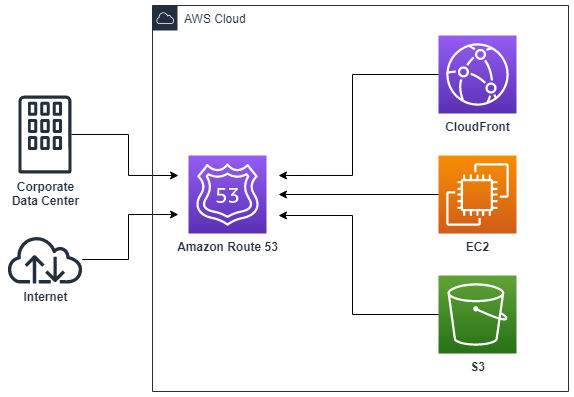
Implementation details
The Hybrid DNS system will integrate AWS Route53 and on-premise DNS servers. Route53 will be used as a primary DNS service, handling traffic routing for both AWS and on-premise resources. On-premise DNS servers will serve as a secondary mechanism, providing a backup for requests and acting as a resolver for on-premise resources.
Route 53 Resolvers
Route 53 Resolver facilitates the resolution of domain names for workloads in Amazon Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs). It enables the routing of DNS queries between VPCs and on-premises networks, as well as among AWS VPCs.
The following are the types of Route 53 Resolvers:
Inbound Resolvers: These are designed to forward DNS queries from an external network to the VPCs. This is achieved by configuring one or more "inbound endpoints" in one or more VPCs. Then, on the network, a DNS resolver is configured to forward DNS queries to the IP addresses for the inbound endpoints.
Outbound Resolvers: These are designed to forward DNS queries from the VPCs to the external network. This involves creating "resolver rules" that specify the domain names for the DNS queries that are to be forwarded, and the IP addresses of the DNS resolvers on the external network.
Routing Policies
Route53 will utilize a combination of routing policies to manage DNS requests. This includes:
Simple Routing Policy: For single resources that perform a given function for your domain.
Failover Routing Policy: In the event of a resource failure, traffic will be redirected to another resource.
Geolocation Routing Policy: Route traffic based on the geographic location of your users.
Latency-Based Routing Policy: Route traffic to the resource that provides the best latency
Security and Compliance
Amazon Route 53 offers robust security features for DNS management. It supports DNSSEC, which validates responses to DNS queries to prevent DNS spoofing. Additionally, it provides DNS Firewall that enhances security by allowing administrators to filter and regulate outbound DNS traffic. Through rule-based DNS filtering, it helps block access to known malicious domains, providing an additional layer of security.
Route 53 Resolver DNS Firewall
Route 53 Resolver DNS Firewall offers an additional layer of protection for VPC resources by allowing network administrators to filter and regulate outbound DNS traffic.
The DNS Firewall enables the creation of rules to block DNS queries to known malicious domains and to allow queries to trusted domains. It also provides detailed query level logs for visibility and auditing purposes. This enhances security, control, and visibility for VPC resources.
Types of DNS Firewall Rules:
Allow: This rule type permits DNS queries for the domain names specified in the rule, and blocks all others.
Block: This rule type blocks DNS queries for the domain names specified in the rule.
Alert: This rule type allows the DNS queries but flags them for review. It's useful for monitoring potentially harmful traffic without interrupting service.
Industrial Standards
PCI DSS Level 1: Route 53 supports the processing, storage, and transmission of credit card data by a merchant or service provider, and has been independently validated to comply with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
SOC (System and Organization Controls): Route 53 is compliant with SOC 1, SOC 2, and SOC 3 requirements. These standards evaluate the design and effectiveness of controls that directly affect customers’ financial reporting, security, availability, and processing integrity of systems, and the privacy of processed data.
HIPAA: Route 53 also aligns with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) standards. This means that it can be used to handle sensitive patient data for organizations that are subject to HIPAA regulations.
Monitoring and Logging
Amazon CloudWatch: Used for tracking Route 53 metrics such as query volume, latency, and error rates, which can aid in diagnosing issues and optimizing performance.
AWS CloudTrail: Logs and monitors account activity, including Route 53 API calls, providing traceability for changes to AWS resources.
Route 53 Resolver Query Logs: Records the DNS queries that Route 53 Resolver receives for a VPC, offering visibility into DNS activity.
DNS Firewall logs: Provides detailed audit logs of every DNS query that Route 53 Resolver answers, aiding in security monitoring and troubleshooting.
Expected Outcomes
Improved Routing: Efficient domain name to IP address translation for enhanced user routing.
Secure Connectivity: Safe linkage between on-premise networks and AWS VPCs.
Enhanced Security: Strengthened protection against DNS spoofing and malicious domains.
Monitoring: Detailed insights into performance and security for prompt troubleshooting.
Compliance: Alignment with key regulations like PCI DSS, SOC, and HIPAA.
Scalability: Adaptability to changes in DNS query volume without extensive manual adjustments.