Agent
Revision | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 24.07.2024 | Init Changelog |
Introduction
Gitlab Agent is an application allowing to integrate Gitlab with Kubernetes. This integration helps to install, configure, manage, deploy and troubleshoot cluster applications.
Currently, Gitlab integrates Flux for GitOps. With GitOps, you can manage containerized clusters and applications from a Git repository that:
Is the single source of truth of system.
Is the single place where you operate system.
By combining Gitlab (with Agent), Kubernetes and Flux, you can have:
Gitlab as the GitOps (Flux) operator.
Kubernetes as the automation and convergence system.
Gitlab CI/CD for Continuous Integration.
The agent for Continuous Deployment and cluster observability.
Build-in automatic drift remediation.
Deployment sequence
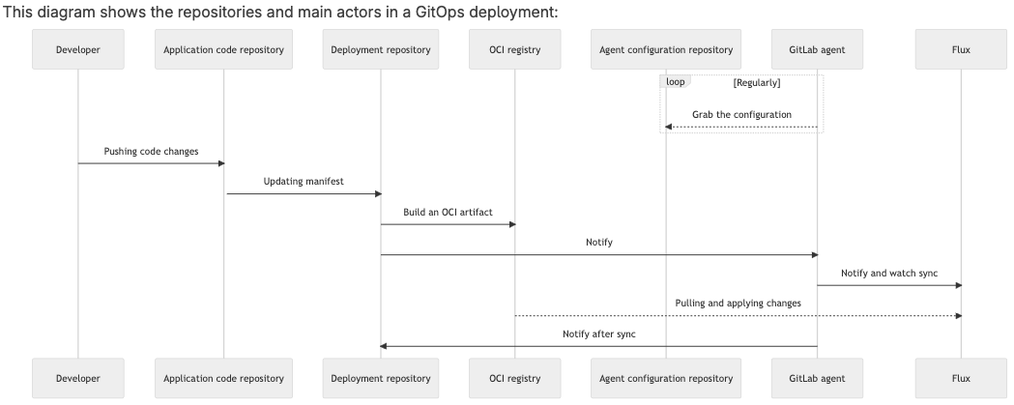
Immediate Git repository reconciliation
Usually, the Flux source controller reconciles Git repositories at configured intervals. This can cause delays between a git push and the reconciliation of the cluster state, and results in unnecessary pulls from GitLab.
The agent for Kubernetes automatically detects Flux GitRepository objects that reference GitLab projects in the instance the agent is connected to, and configures a Receiver for the instance. When the agent for Kubernetes detects a git push, the Receiver is triggered and Flux reconciles the cluster with any changes to the repository.
To use immediate Git repository reconciliation, you must have a Kubernetes cluster that runs:
The agent for Kubernetes.
Flux
source-controllerandnotification-controller.
Immediate Git repository reconciliation can reduce the time between a push and reconciliation, but it does not guarantee that every git push event is received. You should still set GitRepository.spec.interval to an acceptable duration.
Token management
To use certain Flux features, you might need multiple access tokens. Additionally, you can use multiple token types to achieve the same result.
This section provides guidelines for the tokens you might need, and provides token type recommendations where possible.
GitLab access by Flux
To access the GitLab container registry or Git repositories, Flux can use:
A project or group deploy token.
A project or group deploy key.
A project or group access token.
A personal access token.
Example YAML
kustomization.yaml
flux.yaml
Flux to GitLab notification
If you configure Flux to synchronize from a Git source, Flux can register an external job status in GitLab pipelines.
To get external job statuses from Flux, you can use:
A project or group deploy token.
A project or group access token.
A personal access token.
The token requires api scope. To minimize the attack surface of a leaked token, you should use a project access token.
Deployment
To set up Flux for GitOps with Gitlab:
Create a personal access token (or use existing one)
Complete a bootstrap installation
Register
agentkInstall
agentk
Prerequisites
Prerequisites:
You must have a Kubernetes cluster you can access locally with
kubectl.You must install the Flux CLI. Be sure to install Flux v2 or higher.
Create a personal access token
To authenticate with the Flux CLI, create a personal access token with the api scope:
On the left sidebar, select your avatar.
Select Edit profile.
On the left sidebar, select Access Tokens.
Enter a name and optional expiry date for the token.
Select the
apiscope.Select Create personal access token.
You can also use a project or group access token with the api scope. Or create a technical gitlab account.
Complete a bootstrap installation
Follow instruction from this article: [Bootstrap FluxCD].
Upgrade Flux
If you have your cluster with Flux installed, you might need to upgrade Flux. To do it, follow instruction from this article: [Upgrade FluxCD on cluster].
Register agentk
You must register agentk before you install it in your cluster.
To register agentk:
On the left sidebar, select Search or go to and find your project. If you have an agent configuration file, it must be in this project. Your cluster manifest files should also be in this project.
Select Operate > Kubernetes clusters.
Select Connect a cluster (agent).
If you want to create a configuration with CI/CD defaults, type a name.
If you already have an agent configuration file, select it from the list.
Select Register an agent.
Securely store the agent access token and
kasAddressfor later.
The agent is registered for your project. You don’t need to run any commands yet.
In the next step, you’ll use Flux to install agentk in your cluster.
Install agentk
Next, use Flux to create a namespace for agentk and install it in your cluster.
To install agentk:
Create namespace definition in your Flux repository:
namespace.yamlapiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: gitlabAdd secret using plain YAML file (
secret.yaml) or using secretGenerator fromKustomize:secret.yamlapiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: gitlab-agent-token type: Opaque stringData: token: "<your-token-here>"kustomization.yamlsecretGenerator: - name: gitlab-agent-token options: disableNameSuffixHash: true literals: - token=<your-token-here>Add
helm.yamlfile to your Flux repository (theHelmReleaseuses the secret from the previous step):apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1beta2 kind: HelmRepository metadata: labels: app.kubernetes.io/component: agentk app.kubernetes.io/created-by: gitlab app.kubernetes.io/name: agentk app.kubernetes.io/part-of: gitlab name: gitlab-agent namespace: gitlab spec: interval: 1h0m0s url: https://charts.gitlab.ioapiVersion: helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v2beta1 kind: HelmRelease metadata: name: gitlab-agent namespace: gitlab spec: chart: spec: chart: gitlab-agent sourceRef: kind: HelmRepository name: gitlab-agent namespace: gitlab interval: 1h0m0s values: config: kasAddress: "wss://kas.gitlab.com" secretName: gitlab-agent-tokenCommit and push your files to remote and wait till Flux reconciles them.
Verify that
agentkis installed and running in the cluster:
Deploy an example project
You can scale Flux deployments across multiple Gitlab projects by adding a Flux GitRepository and Kustomization that points to another project. You can use this feature to store manifests related to a particular Gitlab group in that group.
To demonstrate, deploy an nginx application and point Flux at it:
In Flux repository commit and push the following code to
example-nginx-app.yaml:example-nginx-app.yaml--- apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1 kind: GitRepository metadata: name: example-nginx-app namespace: flux-system spec: interval: 1m0s ref: branch: main url: https://gitlab.com/example/nginx-app.git --- apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1 kind: Kustomization metadata: name: example-nginx-app namespace: flux-system spec: interval: 10m0s path: ./manifests prune: true sourceRef: kind: GitRepository name: example-nginx-appTo verify that the application was deployed correctly and agentk is running, run the following command:
kubectl -n example-nginx get pods
Active agents
Autopay
Name | Cluster | Namespace | Config File | Attached Repository | YAML Manifest |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| |||
|
|
| |||
|
|
| |||
|
|
| |||
|
|
| |||
|
|
| |||
|
|
| |||
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
Upgrade
For compatibility reasons, the Gitlab Agent version should stay in sync with the Gitlab Server instance (major.minor version only, patch version is dedicated to a specific application).
Auto-patch
Every agent has applied Auto-patch mechanism using FluxCD Helm Controller. This allows keeping a latest version of Helm Chart, with all bug and security fixes done automatically.
Auto-patch works only on a patch version. Not major.minor to keep compatibility with a Gitlab Server version.
Prepare
Before you upgrade Gitlab Agent, you need to check if it’s available. To do this run commands below:
Action
To perform Gitlab Agent upgrade, go through steps below:
Go to FluxCD repository.
Go to
bases/gitlab-agentand change version inhelm.yaml(optional) Modify
valuesif needed in apps - look atclusters/*/apps/gitlab/directories.Commit and push changes.
Wait till FluxCD reconcile release.