Troubleshooting
Revision | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 24.07.2024 | Init documentation |
Introduction
Kubernetes troubleshooting refers to the process of identifying, diagnosing, and resolving issues that occur within a Kubernetes cluster. Kubernetes, as an orchestration platform for containerized applications, can encounter various problems that affect the deployment, operation, and performance of applications. Effective troubleshooting ensures the reliability and stability of the applications running in the cluster.
Common Issues
Pod Failures: Pods may fail to start, crash, or get stuck in a pending state.
Resource Constraints: Nodes may run out of CPU, memory, or other resources, causing pods to be evicted or fail to schedule.
Networking Problems: Issues with network policies, DNS resolution, or inter-pod communication.
Persistent Storage Issues: Problems with volume mounting, storage access, or data persistence.
Configuration Errors: Misconfigurations in deployment files, ConfigMaps, or Secrets.
Cluster Component Failures: Problems with Kubernetes components like the API server, etcd, kube-scheduler, or kubelet.
Performance Bottlenecks: Latency or performance degradation in applications or Kubernetes components.
Visual Guide
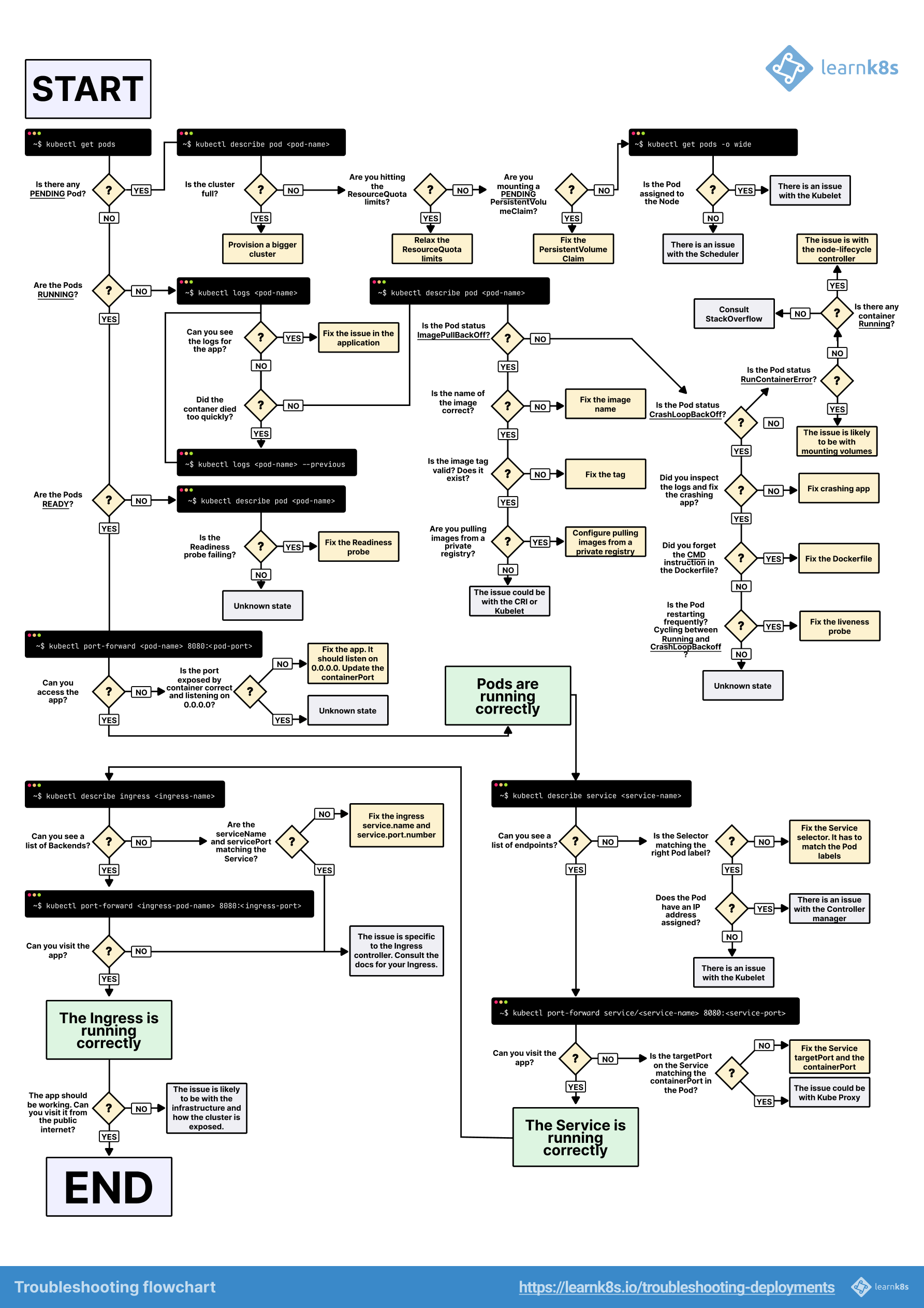
Tools for Kubernetes Troubleshooting
kubectl: The primary command-line tool for interacting with Kubernetes clusters.
K9s: A terminal UI to interact with Kubernetes clusters.
Lens: An IDE for managing Kubernetes clusters.
Prometheus and Grafana: For monitoring and alerting on cluster and application metrics.
Elasticsearch, Fluentd, and Kibana (EFK): For logging and log management.
Jaeger: For distributed tracing and performance monitoring.