LLD003-001 - Continuous Compliance - rules, controls, remediation's
Introduction
Purpose
The purpose of this document is to outline the low-level design architecture for Continuous Compliance, to set up an active monitoring of AWS Infrastructure on organization’s accounts, that reacts to non-compliant resources configurations
Changelog
Revision | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 10.07.2024 | Initial document |
Scope
This document defines configurations of two security services:
AWS Config: specification of rules and conformance packs that will be implemented with custom deployment solution.
AWS Security Hub: specification of benchmarks, controls and remediation's that will be implemented with custom deployment solution.
Definitions
Control: set of rules that are a part of AWS Security Hub Benchmark. Might have its representation in AWS Config as a Config Rule.
Finding: information about detected security issue or potential vulnerability in accounts infrastructure. Findings are generated by AWS Security Hub.
Security Check: the evaluation of a control against a single AWS resource, and it results in a finding that shows the result of the check.
Security Standard: predefined set of security best practices and compliance checks designed to help users enhance the security of their AWS environment. Security Standards in AWS Security Hub consists of a set of "controls".
Architecture Overview
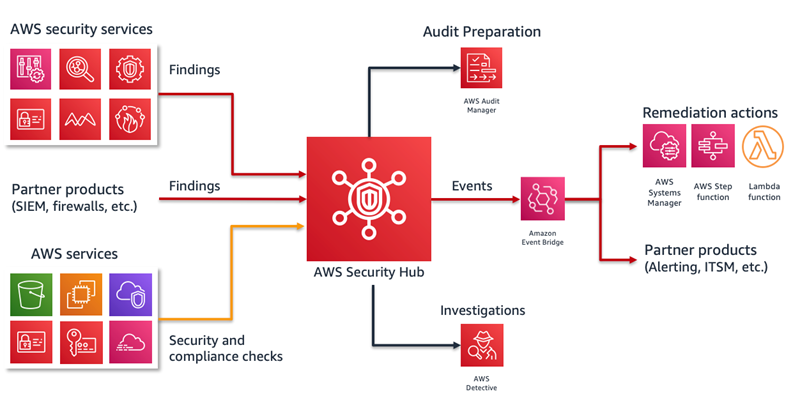
AWS Security Hub will be used as a hub aggregating data from other AWS security services, but also as an additional tool for evaluating compliance, using controls included in Security Hub Benchmarks (Security Standards).
Thanks to integration with Amazon EventBridge, we can set up remediation's for any non-compliance found, with advanced filtering.
AWS Config will be used as a core for Security Hub, by deploying a set of conformance packs, each including dozens of rules. Security Hub will also deploy aprox. 200 AWS Managed Rules with Security Standards. Every non-compliance found in a rule, will be reproduced as a finding in AWS Security Hub.
Every time there is a new finding generated, event is triggered which can be associated with chosen remediation.
More information about High Level Design can be found in document “HLD003 - Continuous Compliance” (will be available soon).
AWS Security Hub Configuration
Overview
AWS prepared predefined Security Standards which includes the list of controls in the standard. Each control includes the following information:
The security category that the control belongs to
The resource that the control applies to
If applicable, the AWS Config rule that is used for the control
Any parameters used by the control
A description of the control and what it checks
For standards that are associated with a regulatory framework, the applicable requirements in that framework
Information on how to remediate a failed check. For example, you might need to change the configuration of a resource.
Security standards and controls
We will use CIS AWS Foundations Benchmark v1.4.0 and AWS Foundational Security Best Practices standards.
CIS AWS Foundations Benchmark v1.4.0 - serves as a set of security configuration best practices for AWS. These industry-accepted best practices provide you with clear, step-by-step implementation and assessment procedures. List of controls with all information, including remediating methods is available here: CIS AWS Foundations Benchmark
AWS Foundational Security Best Practices - a set of automated security checks that detect when AWS accounts and deployed resources do not align with security best practices. The standard is defined by AWS security experts. This curated set of controls helps improve your security posture in AWS, and covers AWS’s most popular and foundational services. This standard consists of aprox. 200 controls: AWS Foundational Security Best Practices (FSBP) standard
Controls to be disabled in case of Multi Region environment
CIS AWS Foundations Benchmark 3.7 control - This control deals with using AWS KMS to encrypt CloudTrail trail logs. Logs will be centralized so control will be active only in the one account and region where centralized logging take place.
CIS AWS Foundations Benchmark 1.4-1.10, 1.12, 1.14, 1.16, 1.17, and 3.5 checks - Have to be disabled on all but one Region to save costs. For example 1.4 root account key check should not be performed on all regions.
CIS AWS Foundations Benchmark 1.7, 4.4-4.14 checks - should be disabled if GuardDuty will be used for anomaly detection.
AWS Foundational Best Practices controls - in case of global services like IAM some controls should be used only in one Region, if not checks for the same resources will be executed multiple times what will generate additional costs and remediation's duplicates. In order to avoid these issues controls below should be disabled on all Regions except the region that records global resources:
Disabled controls
Some controls will be disabled on clients request or to avoid issues like finding duplication with AWS Config, due to wrong parameters' configuration.
Disabled list:
[IAM.8] Unused IAM user credentials should be removed - disabled due to wrong parameter value. Instead, rule iam-user-unused-credentials-check will be deployed with parameter maxCredentialUsageAge set to 30 in AWS Config.
[EC2.3] Attached Amazon EBS volumes should be encrypted at-rest - disabled on tst and dev environments on client's request.
[EC2.23] Amazon EC2 Transit Gateways should not automatically accept VPC attachment requests
Not Supported Manual Checks
Security Hub focuses on automated security checks. As a result, Security Hub doesn't support the following requirements of CIS AWS Foundations Benchmark v1.4.0 because they require manual checks of your resources:
1.1 – Maintain current contact details
1.2 – Ensure security contact information is registered
1.3 – Ensure security questions are registered in the AWS account
1.11 – Do not set up access keys during initial user setup for all IAM users that have a console password
1.18 – Ensure IAM instance roles are used for AWS resource access from instances
1.21 – Ensure IAM users are managed centrally via identity federation or AWS Organizations for multi-account environments
2.1.4 – Ensure all data in Amazon S3 has been discovered, classified and secured when required
5.4 – Ensure routing tables for VPC peering are "least access"
Not Supported Automated Checks
Security Hub doesn't support the following requirements of CIS AWS Foundations Benchmark v1.4.0 that rely on automated checks:
1.13 – Ensure there is only one active access key available for any single IAM user
1.15 – Ensure IAM users receive permissions only through groups
1.19 – Ensure that all the expired SSL/TLS certificates stored in IAM are removed
1.20 – Ensure that IAM Access Analyzer is enabled for all Regions
2.1.3 – Ensure MFA Delete is enabled on S3 buckets
3.10 – Ensure that Object-level logging for write events is enabled for S3 bucket
3.11 – Ensure that Object-level logging for read events is enabled for S3 bucket
4.1 – Ensure a log metric filter and alarm exist for unauthorized API calls
4.2 – Ensure a log metric filter and alarm exist for Management Console sign-in without MFA
4.3 – Ensure a log metric filter and alarm exist for usage of
rootaccount (this is similar to automated requirement 1.7 – Eliminate use of the 'root user for administrative and daily tasks, which is supported in Security Hub)4.15 – Ensure a log metric filter and alarm exists for AWS Organizations changes
5.2 – Ensure no security groups allow ingress from
0.0.0.0/0to remote server administration ports
Deployment
Deployment of Security Hub will be executed using custom AWS Security Hub Solution. Solution consists of few steps that needs to be done in order to implement AWS Security Hub, its resources and remediations:
write a configuration template for the organization that specifies:
which controls and standards are enabled/disabled (per-account)
which remediations are active for which controls
and, optionally, rules for automatic suppression of findings based on tags/finding details/resource ids
run the Terragrunt solution on global repository
Solution will be deployed on all accounts except “Sandbox” accounts. Aggregator is not planned due to lack of permissions for delegated administrator of AWS Security Hub service.
Solution consists of a few terraform modules. The main module takes care of activation of standards and suppressing controls. The rest of the modules are responsible for remediation's. Each module is one remediation type. Solution supports adding new remediations as modules in the future.
AWS Config configuration
Overview
AWS Config is a service that allows for the evaluation and audit of AWS resources. It continuously monitors the configurations of resources and evaluates their compliance with policies using selected rules.
AWS Config solution will be responsible for deployment of 6 conformance packs:
OperationalBestPracticesForSecurityServices
OperationalBestPracticesForEncryptionAndKeys
OperationalBestPracticesForStorageServices
AdditionalSecurityComplianceChecks
ISO27001ConformancePack
TagEnforcingConformancePack
Descriptions of rules can be found here: Rules List
Conformance Packs and Rules
Rules in these conformance packs are supplementary to controls in AWS Security Hub Benchmarks.
Each Conformance Pack consists of a set of rules. Some rules require defining parameters.
OperationalBestPracticesForSecurityServices
Set of rules that checks best practices
A set of rules that checks for best practices related to security and security monitoring services such as: CloudTrail, GuardDuty, IAM, Secret Managers, and SecurityHub.
Below is a list of rules in this conformance pack with their parameters and corresponding values:
account-part-of-organizationsacm-certificate-expiration-check:daysToExpiration: 60
guardduty-enabled-centralizedguardduty-non-archived-findings:daysLowSev: 30
daysMediumSev: 7
daysHighSev: 1
iam-group-has-users-checkiam-password-policy:RequireUppercaseCharacters: true
RequireLowercaseCharacters: true
RequireSymbols: true
RequireNumbers: true
MinimumPasswordLength: 20
PasswordReusePrevention: 24
MaxPasswordAge: 90
iam-user-group-membership-checksecurityhub-enabledwafv2-logging-enabledsecretsmanager-secret-periodic-rotation:maxDaysSinceRotation: 90
iam-user-unused-credentials-check(replacing IAM.8 Security Hub control due to shorter maxCredentialUsageAge):maxCredentialUsageAge: 30
OperationalBestPracticesForEncryptionAndKeys
A set of rules that checks for best practices related to encryption and keys.
Below is a list of rules in this conformance pack with their parameters and corresponding values:
api-gw-cache-enabled-and-encryptedelasticsearch-node-to-node-encryption-checkelbv2-acm-certificate-requiredsagemaker-endpoint-configuration-kms-key-configuredsagemaker-notebook-instance-kms-key-configuredRdsClusterStorageEncryptedElasticacheRedisEncryptedAtRestElasticacheRedisTransitEncryptiondynamodb-table-encryption-enabledkinesis-stream-encryptedapi-gw-ssl-enableds3-default-encryption-kms
OperationalBestPracticesForStorageServices
A set of rules that checks for best practices related to data storage services, focused mainly on backups.
Below is a list of rules in this conformance pack with their parameters and corresponding values:
fsx-resources-protected-by-backup-planstoragegateway-resources-protected-by-backup-planvirtualmachine-resources-protected-by-backup-plandynamodb-in-backup-planrds-resources-protected-by-backup-planrds-in-backup-planec2-resources-protected-by-backup-plan
AdditionalSecurityComplianceChecks
A set of rules that checks for best practices related to security and log collection. This is a package that extends the "OperationalBestPracticesForSecurityServices".
Below is a list of rules in this conformance pack with their parameters and corresponding values:
emr-kerberos-enabledcloudtrail-s3-dataevents-enabledcloudtrail-security-trail-enabledcloudwatch-alarm-action-check:alarmActionRequired: true
insufficientDataActionRequired: true
okActionRequired: true
cw-loggroup-retention-period-check:MinRetentionTime: 90
restricted-ssh(ID:INCOMING_SSH_DISABLED)ec2-instances-in-vpc(ID:INSTANCES_IN_VPC)ec2-no-amazon-key-pairec2-volume-inuse-checkecs-task-definition-nonroot-userecs-task-definition-memory-hard-limitautoscaling-capacity-rebalancingeks-endpoint-no-public-accessapproved-amis-by-tag:amisByTagKeyAndValue: "hardened:true"
CheckSNSEmailSubscribers:domain_regex: “^.*?t-mobile\.pl$”
ISO27001ConformancePack
A set of rules that checks if AWS resources comply with ISO27001 standards.
Below is a list of rules in this conformance pack with their parameters and corresponding values:
EksAuditLoggingEnabledRuleNoEC2InstanceOlderThanYear:Age: 365
AccessAnalyzerNoFindingsACMCertificateTransparencyLoggingAllElasticLoadBalancersAreNotInternetFacingAmisArePrivateCheckTrustedAdvisorCloudtrailLogsBucketIsPrivateEc2SnapshotsAreEncryptedEcrReposArePrivateEcrScanFoundVulnerabilitiesIAMUserActiveKeysLambdasInvokeAPICloudtrailPublicHostedZonesLoggingSecurityGroupNoEmptyIngressSgHasNoPublicIngressSNSAccessNotPublicSQSAccessNotPublicSqsEncryptedAtRestSsmSessionDocumentsHaveLoggingeip-attachedec2-instance-profile-attached
TagEnforcingConformancePack
A set of rules that checks if AWS resources are tagged according to established policies.
Tags that will be checked by rules are defined according to Naming and Tagging convention document.
Below is a list of checked resource types. Each resource type has its own rule:
AWS::EC2::CustomerGatewayAWS::EC2::InternetGatewayAWS::EC2::RouteTableAWS::EC2::SubnetAWS::EC2::VPCAWS::EC2::VPNConnectionAWS::EC2::VPNGatewayAWS::EC2::InstanceAWS::EC2::SecurityGroupAWS::EC2::NatGatewayAWS::EC2::TransitGatewayAWS::EC2::VPCEndpointAWS::EC2::VPCEndpointServiceAWS::EC2::VPCPeeringConnectionAWS::RDS::DBInstanceAWS::RDS::DBClusterAWS::EKS::ClusterAWS::ECS::ClusterAWS::Lambda::FunctionAWS::S3::BucketAWS::DynamoDB::TableAWS::AutoScaling::AutoScalingGroupAWS::ElasticLoadBalancingV2::LoadBalancer
Additional AWS Config Custom Rules
As requested, additional custom rule will be created:
CheckSNSEmailSubscriber- This rule checks if the domain of email subscribers for an SNS Topic matches the parameter provided in the form of a regular expression. For example, using the regex pattern^.*?tameshi\.pl$will validate if the subscribers' email addresses originate from thetameshi.pldomain.
Rule will be included in AdditionalSecurityComplianceChecks conformance pack.
Deployment
Due to AWS Config requirements to use Cloudformation templates for Conformance Packs definitions, the whole solution is written in CloudFormation with terraform and terragrunt used as a wrapper. Solution uses universal template that will be applied on all accounts except “Sandbox” accounts.
Solution will be deployed with Terragrunt on global repository.
Changing and applying modified templates will result in conformance packs redeployment.
Remediations
We will use Security Hub findings events as a trigger for automatic remediations.
In most cases automatic remediations should be focused on sending notification about found issue (finding) with Simple Email Service or Simple Notification Service. For sending notifications with emails we will use SES Identity deployed on “Shared-Services” account. That identity will be used as a delegated sender by Security Hubs on all organization’s accounts.
AWS Services used in remediations:
Amazon EventBridge - triggering AWS Lambda Functions in reaction to new Findings in Security Hub
AWS Lambda - executing remediations logic
Simple Email Service - sending emails with information about non-compliant resources
SES Email Notification Remediation
We will use automatic remediations in form of SES email notification for Security Hub controls:
CIS AWS Foundations Benchmark v1.4.0:
[IAM.3] Ensure access keys are rotated every 90 days or less
[EC2.6] Ensure VPC flow logging is enabled in all VPCs
AWS Foundational Security Best Practices:
[DynamoDB.3] dax-encryption-enabled
[ELB.1] alb-http-to-https-redirection-check
[EFS.1] efs-encrypted-check
[ES.1] elasticsearch-encrypted-at-rest
[EC2.3] encrypted-volumes
[Opensearch.1] opensearch-encrypted-at-rest
[Opensearch.3] opensearch-node-to-node-encryption-check
[RDS.3] rds-storage-encrypted
[RDS.4] rds-snapshots-encrypted
[Redshift.2] redshift-require-tls-ssl
[Redshift.10] redshift-cluster-kms-enabled
[S3.4] s3-bucket-server-side-encryption-enabled
[SNS.1] sns-encrypted-kms
[SSM.4] ssm-document-not-public
We will use automatic remediations in form of SES email notification for findings originating from AWS Config rules:
TagEnforcingConformancePack - all rules within conformance pack
OperationalBestPracticesForEncryptionAndKeys - all rules within conformance pack
List of rules in conformance packs available here: Conformance Packs Description
Remediation workflow
SES Email remediation will send email to:
resource creator (email taken from resource tag "creator"),
if step 1 fails then email will be sent to owner (taken from tag "owner")
if step 2 fails then the email will be sent to Cloud team responsible for given environment.
Last step will be omitted for environments test and dev.
Unused Credentials Remediation
We will deploy rule iam-user-unused-credentials-check twice - one with parameter checking if credentials were unused for past 30 days, and second rule with parameter checking if credentials were unused for past 60 days. First rule is prepared for future notifications, while second rule will trigger Lambda Function, through EventBridge rule, responsible for deactivating credentials unused for more than 60 days
Findings to OpenSearch Remediation
Every time there is a new finding in Security Hub, EventBridge notices it and passes findings data to Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose. Kinesis then gathers new findings for specified amount of time (5 minutes), compresses data and sends them to centralised S3 bucket for Opensearch ingestion. Using Kinesis instead of simple Lambda Function for this remediation has its advantages. The first one is data aggregation. Most new findings will show up during deployment of application/infrastructure, since most rules evaluates new resources and changes in already existing ones. It means that most findings show up in first few minutes after deployment. Lambda Function would have to separately upload each new finding to S3 Bucket, while Kinesis gathers them for few minutes, then compresses them together and puts a whole batch as a single object in a bucket. This results in lower amount of data and fewer operations to monitor. Kinesis also automatically scales, while with Lambda there would be possibility of hitting concurrency limit during big deployments and would require additional monitoring and fine tuning.
Pricing
Security Hub
Security checks | Pricing |
|---|---|
First 100,000 checks/account/region/month | $0.0010 per check |
Next 400,000 checks/account/region/month | $0.0008 per check |
Over 500,000 checks/account/region/month | $0.0005 per check |
A security check is the evaluation of a control against a single AWS resource, and it results in a finding that shows the result of the check. You are charged per number of checks per account per region. You are only charged once for a check when controls that are shared across different standards are evaluated against the same resource.
Ingested Findings | |
|---|---|
Ingested findings associated with Security Hub's security checks | free |
First 10,000 events/account/region/month | free |
Over 10,000 events/account/region/month | $0.00003 per event |
AWS Security Hub ingests findings from various AWS services and partner products. Finding ingestions include both new findings and updates to existing findings. You are not charged for finding ingestion's associated with Security Hub' s security checks. You are charged based on the number of other findings sent to Security Hub per account per region each month. Security Hub offers a perpetual free tier of 10,000 findings per account per Region per month.
Estimates
It is not possible to accurately estimate the costs of the service. That's because pricing is strictly correlated with the number of resources and amount of workload and changes taking place in AWS account. Basing on migration experience, there are around 60000 ingested findings in single account's region monthly (you are only billed per region you are working on). There are also 20000 security checks per region on average.
Findings Ingested:
The free tier includes the first 10,000 findings ingested monthly per account per region. Given volume of 60,000 findings, the first 10,000 would be free, and the remaining 50,000 would be billed at a rate of $0.00003 per finding. This results in a monthly cost of $1.50 for findings ingested.
Security Checks: For 20,000 security checks performed monthly, the cost would be $20 per account per month, calculated at a rate of $0.001 per security check.
20000 * $0.001 = $20
With these considerations, the total estimated cost for AWS Security Hub, given described usage, would be $21.50 per account per region per month.
AWS Config
You pay $0.003 per configuration item recorded in your AWS account per AWS Region. A configuration item is recorded whenever a resource undergoes a configuration change or a relationship change. The resource could be an AWS, third-party, or custom resource. Additionally, you pay for every executed evaluation of configuration item.
Conformance pack evaluations | Price |
|---|---|
First 100,000 conformance pack evaluations | $0.001 per conformance pack evaluation per Region |
Next 400,000 conformance pack evaluations (100,001-500,000) | $0.0008 per conformance pack evaluation per Region |
500,001 and more conformance pack evaluations | $0.0005 per conformance pack evaluation per Region |
A conformance pack evaluation is defined as an evaluation of a resource by an AWS Config rule within the conformance pack. Every rule deployed in AWS Config, that is not managed by Security Hub, will be a part of Conformance Pack.
Additional costs might be added for AWS Lambda Functions. Custom AWS Config rules use Lambda Functions for resources evaluation.
Estimates
It is not possible to accurately estimate the costs of the service. That's because pricing is strictly correlated with the number of resources and amount of workload and changes taking place in AWS account. Basing on migration experience, there are around 30000 resource changes in single account's region monthly (you are only billed per region you are working on). This result in creation of 30000 configuration items. Each configuration item, on average, triggers evaluation of two rules in conformance pack.
Configuration Items recordings:
30000 items * $0.003 = $90 per month per region
Conformance Pack evaluations:
30000 items * 2 evaluations per item * $0.001 = $60 per month per region
So, with 30000 resource changes, your total AWS Config cost on a single accounts region equals $150
Remediations
Costs of remediations depends on the remediations themselves. In most cases Security Hub remediations are based on Lambda Functions, so pricing for AWS Lambda service applies.
https://aws.amazon.com/lambda/pricing/
When it comes to Kinesis, the costs should also be close to none. In order for kinesis to generate costs in ranges above one dollar in “Findings to Opensearch remediation”, Security Hub would have to find hundreds of thousands of new findings, which is very unlikely to occur in well architected infrastructure.