LLD001-002 - Secret keeping policy
Introduction
Purpose
The main goal of this document is to offer a thorough explanation of AWS Secret Manager, which serves as a secrets management service designed to safeguard access to your applications, services, and IT resources. This service simplifies the process of rotating, handling, and retrieving database credentials, API keys, and other confidential information at every stage of their existence.
Changelog
Revision | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 02.07.2024 | Initial document |
Related documents
Background
AWS Secrets Manager is a secrets management service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that helps you protect access to your applications, services, and IT resources. This service is without the upfront investment and ongoing maintenance costs of operating your own infrastructure.
As the name suggests, the Secrets Manager allows you to easily rotate, manage, and retrieve database credentials, API keys, and other secrets throughout their lifecycle. This can help you meet your security and compliance requirements.
Here are some of the key features of AWS Secrets Manager:
Secrets Rotation: AWS Secrets Manager enables you to replace secrets automatically without any risk of disrupting your applications. Secrets rotation is supported for Amazon RDS, Amazon DocumentDB, and Amazon Redshift.
Secure and Manage Secrets: Secrets Manager protects access to applications, services, and IT resources. This can eliminate the upfront investment and ongoing maintenance costs of operating your own infrastructure.
Fine-Grained Access Control: You can configure IAM and resource-based policies to control who can access your secrets. This allows you to follow the principle of least privilege and reduce the risk of unauthorized access to your secrets.
Audit and Monitor Secrets: Secrets Manager events are integrated with AWS CloudTrail. You can use the recorded information to audit secrets, monitor the rotation of secrets, and respond to secret changes.
Pay as You Go: With Secrets Manager, there is no upfront cost, and you pay only for the secrets you store and for the use of these secrets. Secret Manager pricing.
Automatic replication of secrets to multiple AWS Regions: By utilizing AWS Secrets Manager, you have the capability to effortlessly duplicate your confidential information across various AWS Regions, addressing your specific needs for disaster recovery and redundancy between regions. Simply designate the AWS Regions where duplication is necessary, and Secrets Manager will securely generate replicas in those regions. This eliminates the necessity of managing a complicated solution for achieving this functionality. By granting your multi-Region applications access to the duplicated secrets in the designated Regions, you can rely on Secrets Manager to ensure that the replicas remain synchronized with the primary secret.
Programmatic retrieval of secrets: When developing your applications, prioritize the security of your secrets as a key consideration. Secrets Manager offers code samples for invoking its APIs in popular programming languages. Additionally, you can configure Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) endpoints to ensure that communication between your VPC and Secrets Manager remains within the secure AWS network. To further enhance performance and availability when retrieving secrets, you have the option to utilize Secrets Manager client-side caching libraries. These libraries help improve availability by caching secrets on the client side, reducing latency and enhancing overall retrieval efficiency.
Integration with AWS services: AWS Secrets Manager integrates with other AWS services like AWS Lambda, AWS CloudFormation, Amazon RDS, Amazon Redshift, Amazon DocumentDB, and others. Full list of supported services.
Architecture diagram
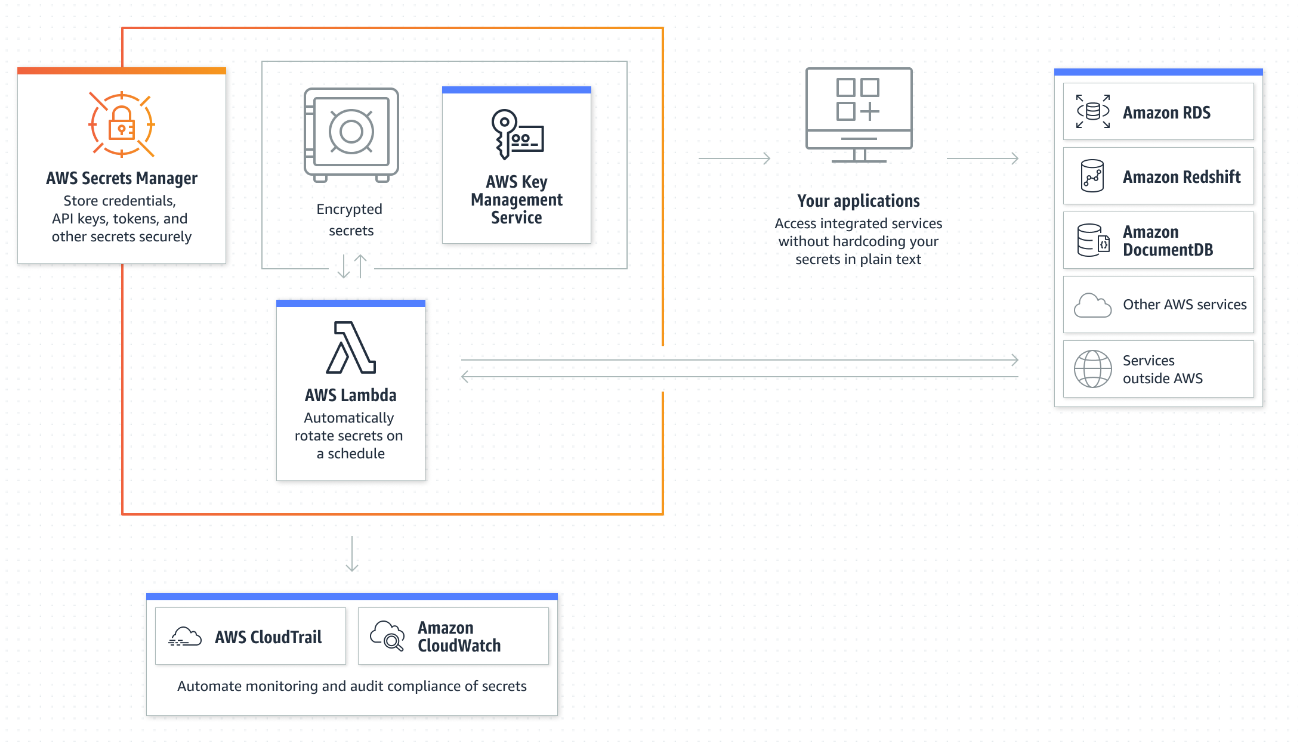
The diagram portrays the main characteristics of AWS Secrets Manager and how it interfaces with other AWS services.
AWS Secrets Manager stores credentials, API keys, tokens, and other secrets securely. Secrets Manager implements a security measure called envelope encryption, which leverages AWS Key Management Service (KMS) keys and data keys to safeguard each secret value. When a secret value undergoes a change, Secrets Manager initiates a request to AWS KMS for a fresh data key to ensure its protection. This approach ensures that secrets remain securely encrypted throughout their lifecycle, with Secrets Manager actively managing the encryption process by collaborating with AWS KMS.
To rotate a secret, Secrets Manager calls a Lambda function according to the schedule you set up. You can set a schedule to rotate after a period of time, for example, every 30 days, or you can create a cron expression.
AWS CloudTrail records all API calls for Secrets Manager as events, including calls from the Secrets Manager console, as well as several other events for rotation and secret version deletion. For a list of the log entries Secrets Manager records, see CloudTrail entries.
You can monitor AWS Secrets Manager using Amazon CloudWatch, which collects raw data and processes it into readable, near-real-time metrics. you can use CloudWatch to alert you when your request rate for APIs or the number of secrets in your account reaches a specific threshold. You can also use CloudWatch to monitor estimated Secrets Manager charges.
Moving the secret to Secrets Manager solves the problem of the secret being visible to anyone who sees the code, because going forward, your code retrieves the secret directly from Secrets Manager. Rotating the secret revokes the current hardcoded secret so that it is no longer valid.
Implementation Details
AWS Secrets Manager can be implemented using two methods: through Terraform or by directly creating secrets using the AWS Management Console.
One option is to utilize Terraform, which allows you to define and manage your AWS Secrets Manager resources programmatically. By creating a Terraform configuration file, and specifying the necessary details and settings, you can deploy and manage secrets in a reproducible and version-controlled manner.
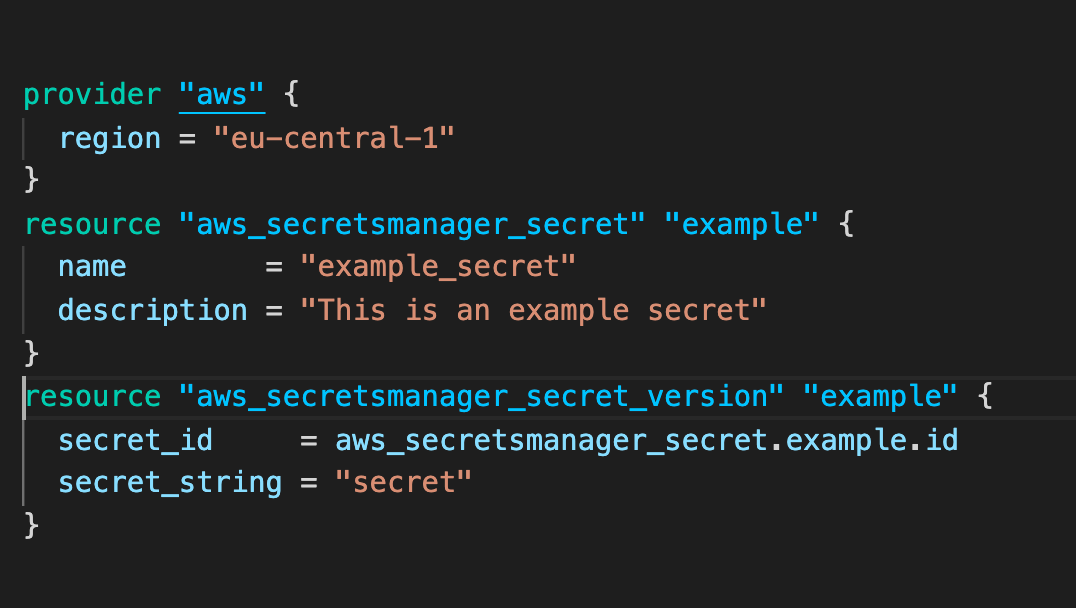
The provided code initially sets up the AWS provider for Terraform to facilitate resource management. Subsequently, it defines a secret named example_secret within AWS Secrets Manager. Additionally, a description is included to provide further details about the secret.
To establish a specific version of the secret, the code employs the aws_secretsmanager_secret_version resource. In this particular instance, the secret_string attribute is assigned the value supersecret.
Alternatively, you can opt to create secrets directly through the AWS Management Console. This approach involves logging into the console, navigating to the AWS Secrets Manager service, and manually creating the secrets by providing the required information and configurations.
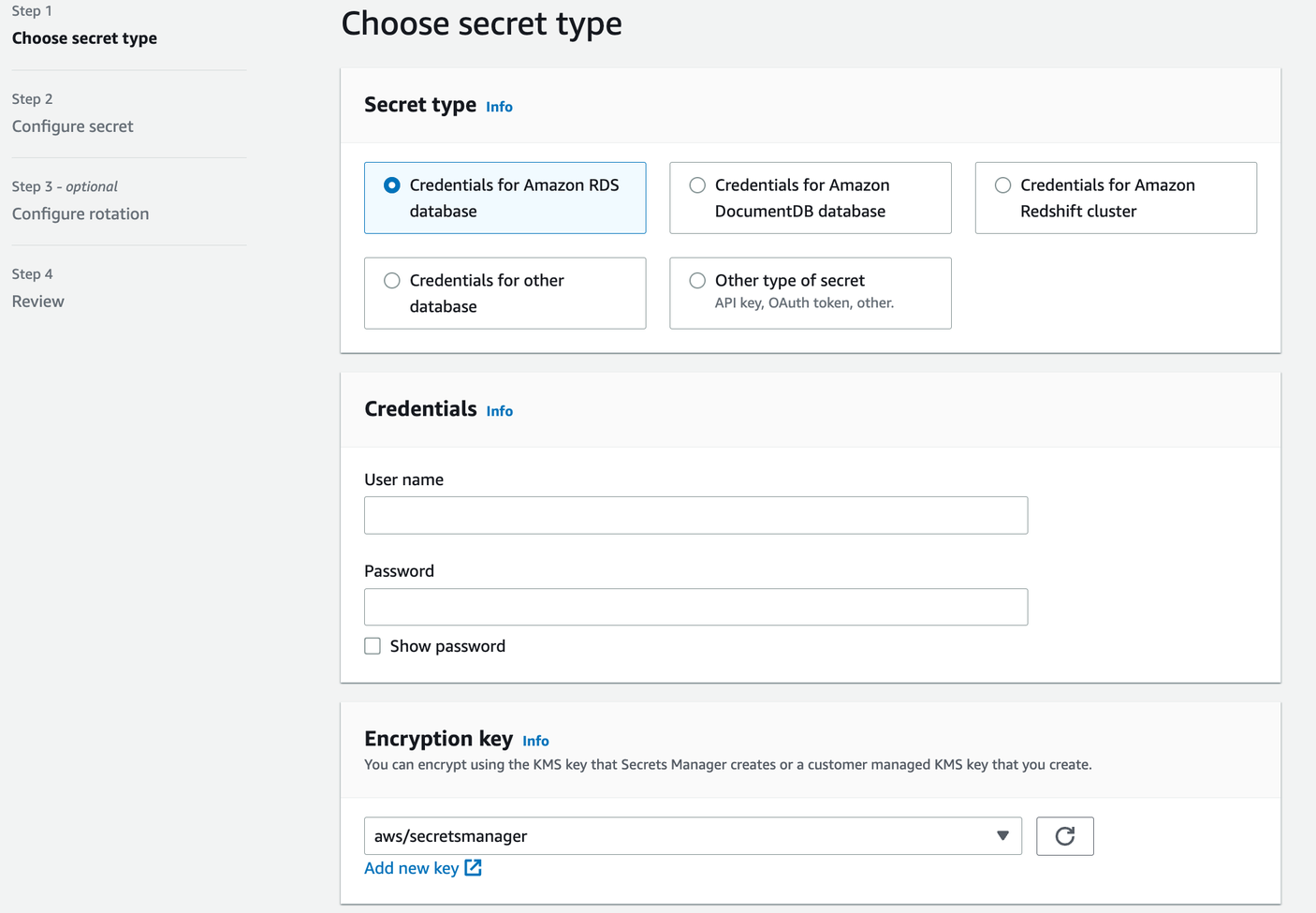
Both methods offer flexibility in implementing AWS Secrets Manager, allowing you to choose the approach that aligns with your preferences and requirements.
Expected Outcomes
We aim to employ the Secret Manager, a tool designed to securely hold critical information for specific application accounts, along with infrastructure secrets on distinct infrastructure accounts. By segregating application and infrastructure secrets, we enhance our system's security. To streamline our development process, these application secrets should be readily accessible to our Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) pipelines through cross-account access. This setup will facilitate smoother operations, promote a robust security posture, and enable efficient, automated deployment workflows.